Spring Boot 备忘
段子: 不管什么业务,直接上一套:spring boot+mysql 集群分库分表读写分离主备切换+kafak 集群+redis 集群用于缓存或者分布式锁+prometheus grafana 性能监控+ELK 日志收集分析+Flink 与 Hive 流批数仓+k8s 部署+双机房容灾
https://github.com/YunaiV/SpringBoot-Labs
记录springboot学习中的问题, 总结; https://github.com/h2pl web 项目 https://github.com/dreamhead/moco mock 框架
https://github.com/cloudfavorites/favorites-web 单体应用实例 hibernate jpa
https://github.com/xkcoding/spring-boot-demo springboot demos
- 1. 常用命令
- 2. 部署脚本
- 3. 工具类
- 4. 和 react 一起打包
- 5. Spring Boot中的注解
- 6. 常用扩展点
- 7. context 上下文 手动注册bean
- 8. 实现事件驱动
- 9. 优雅停机 关机
- 10. 静态注入
- 11. 使用starter
- 12. 监控 and 安全
- 13. 日志
- 14. cqrs模式
- 15. 数据层
- 集成 elasticSearch es
- 集成 influxdb
- 15.1. canal 订阅
- 15.2. mybatis 自动建表插件
- 15.3. mybatis crud 增强插件
- 15.4. 数据库迁移版本控制
- 15.5. 数据库连接字符串收集
- 15.6. graphql集成
- 15.7. 启动执行 SQL
- 15.8. 整合 spring jdbc
- 15.9. 整合 hibernate (即 jpa)
- 15.10. 整合 mybatis-plus
- 15.11. 整合 mybatis
- 15.12. 事务
- 15.13. 缓存
- 15.14. 配合 h2 数据库进行开发
- 15.15. 多数据源
- 15.16. 多数据库类型 databaseIdProvider
- 15.17. spring kafka
- 16. web 相关
- 16.1. 加解密
- 16.2. springboot 发送 https 或者 http 客户端 client
- 16.3. RequestContextHolder
- 16.4. 解决 api 版本共存
- http文件传输操作
- 16.5. 接收参数相关的注解
- 16.6. 自定义接收参数类型
- 16.7. 返回图片
- 16.8. rest api 文档
- 16.9. 过滤器 和 拦截器
- 16.10. servlet Druid 监控
- 16.11. aop 整合使用
- 16.12. controllerAdvice 使用
- 16.13. 利用 ResponseBodyAdvice requestbodyadvice
- 16.14. HttpServletRequest 的输入流只能读取一次的问题
- 16.15. 路由处理
- 16.16. spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
- 17. 运维部署
- 18. spring boot 中的并发
- 19. 实现乐观锁悲观锁
- 20. 移动端消息推送
- 21. 即时通信 IM系统
- 22. 辅助工具
- 23. 校验
- 24. runner 获取命令行参数
- 25. 开发命令行应用
- 26. 整合 grpc
- 27. 任务调度
- 28. 配置文件 and 环境
- 29. 国际化 i18n
- 30. 序列化 反序列化
- 31. 接入第三方支付
- 32. 轻量级的技术栈
- 33. 拾遗
1. 常用命令
du -sh *.jar # jar size
# 打包时没有指定主类,执行可以用java -cp {xxx.jar} {主类名称(绝对路径)}。
# -cp 指定类运行所依赖其他类的路径,通常是类库和jar包,
# 等价 -classpath
# 多个jar包之间连接符:window上分号“;”.Linux下使用“:”
#
# win
java -cp .;d:\work\other.jar;d:\work\my.jar packname.mainclassname
# linux
java -cp .:/hone/myuser/work/other.jar:/hone/myuser/work/my.jar packname.mainclassname
# 表达式支持通配符
java -cp .;c:\work\my.jar;c:\work\*.jar packname.mainclassname
# 打包时指定了主类,执行可以直接用java -jar {xxx.jar}。
# 会用到目录META-INF\MANIFEST.MF文件,在该文件中,有一个叫Main-Class的参数,它说明了java -jar命令执行的类
# java -jar方式不可以指定附加依赖jar包。
java -jar *.jar
# 依赖多个 jar 不使用通配符也可以这样执行
# -D 设置系统属性, 通过System.getProperty("conf1");获得这个值
java -Djava.ext.dirs=lib MyClass
# 跳过测试
# -D 表示 maven 中的 properties
mvn -Dmaven.test.skip=true clean package # skip unit test
mvn -DskipTests clean package
mvn clean package -Pxxx # 指定要激活 maven profile 的 id
java -Dserver.port=8010 -jar xxx.jar # specific server port
java -jar *.jar --server.port=8010 # 同上
# 指定 profile
java -jar *.jar --spring.properties.active=dev
java -jar -Dspring.profiles.active=dev demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
mvn spring-boot:run -Drun.profiles=dev
2. 部署脚本
#!/bin/bash
#本脚本基本无需改动,注意要点均已用中文说明
# 1. 请将本脚本放到Linux系统的path路径下,最好是/bin目录下
# 2. 请给本脚本设备可执行权限
# 3. 启动示例 springboot-starter xxx.jar start
# 4. 重启示例 springboot-starter xxx.jar restart
# 5. 停止示例 springboot-starter xxx.jar stop
# 6. 查看状态示例 springboot-starter xxx.jar status
## 获取 java 命令的路径
JAVA_CMD=`which java`
if [ -z "${JAVA_CMD}" ];then
echo "Please install the Java environment";
exit 1;
fi
## 输出本命令的使用方法 并退出
usage() {
echo "Usage: springboot-starter [app_name].jar [start|stop|restart|status]"
exit 1
}
## 判断是否输入了两个参数
if [ $# -lt 2 ]; then
usage
fi
## 脚本名称
APP_NAME=$1;
## 操作
OPERATION=$2;
## 运行模式
MODEL=$3
if [ -z "$MODEL" ]; then
MODEL="production"
fi
## 其它参数处理
OTHER_ARGS=""
if [ $# -gt 3 ]; then
shift 3
else
shift $#
fi
for ARG in $*
do
OTHER_ARGS="$OTHER_ARGS $ARG"
done
## 脚本所在目录,绝对路径表示
BASE_PATH=$(cd `dirname $APP_NAME`;pwd)
## 去掉所有目录后的脚本名
APP_NAME=${APP_NAME##*/}
## 脚本的路径,绝对路径表示
APP_PATH=$BASE_PATH"/"$APP_NAME
## 判断目标程序是否已经启动
is_running(){
## 尝试获取已经运行程序的PID
PID=`ps -ef|grep ${APP_PATH}|grep -v grep|awk '{print $2}'`
if [ -z "${PID}" ]; then
return 0
else
return 1
fi
}
## 启动程序
start(){
is_running
if [ $? -eq "1" ]; then
echo "${APP_NAME} is already running. pid is ${PID} ."
else
## 启动 jar 包
echo "${APP_NAME} starting ...... "
nohup ${JAVA_CMD} -jar ${OTHER_ARGS} -Dspring.profiles.active=${MODEL} ${APP_PATH} > /dev/null 2>&1 &
echo "nohup ${JAVA_CMD} -jar ${OTHER_ARGS} -Dspring.profiles.active=${MODEL} ${APP_PATH} > /dev/null 2>&1 &"
sleep 1
echo "${APP_NAME} started completed "
echo ""
fi
}
## 停止程序
stop(){
is_running
if [ $? -eq "1" ]; then
echo "PID is ${PID}, ${APP_NAME} stopping ...... "
kill ${PID}
if [ $? -ne "0" ]; then
echo "kill ${PID} failed,execute kill -9 ${PID}"
kill -9 ${PID}
fi
sleep 1
echo "${APP_NAME} stopped completed "
else
echo "${APP_NAME} is not running"
fi
}
## 输出程序运行状态
status(){
is_running
if [ $? -eq "1" ]; then
echo "${APP_NAME} is running. pid is ${PID}"
else
echo "${APP_NAME} is NOT running."
fi
}
## 重启程序
restart(){
stop
start
}
case "$OPERATION" in
"start")
start ;;
"stop")
stop ;;
"status")
status ;;
"restart")
restart ;;
*)
usage ;;
esac
exit 0
3. 工具类
3.1. Apache common
Apache Commons是对JDK的拓展
3.1.1. common-io
FileUtils 文件操作工具类
文件夹操作:
copyDirectory/deleteDirectory/cleanDirectory/getTempDirectory/getTempDirectoryPath
moveDirectory/moveDirectoryToDirectory/moveFileToDirectory/moveToDirectory
forceMkdir/getUserDirectory/getUserDirectoryPath
文件操作:
touch/copyFile/copyURLToFile/moveFile/deleteQuietly/forceDelete/forceDeleteOnExit
toFile/toFiles/toURLs
isFileNewer/isFileOlder
readLines/readFileToByteArray/readFileToString/lineIterator/openOutputStream
write/writeLines/writeByteArrayToFile/writeStringToFile/openInputStream
其他操作:
iterateFiles/listFiles/contentEquals/sizeOf/sizeOfDirectory
FilenameUtils 文件名工具类
获取:
getName/getBaseName/getPrefix/getPrefixLength/getExtension
getPath/getFullPath/getFullPathNoEndSeparator/getPathNoEndSeparator
判断:
isExtension/equals/equalsNormalized/equalsOnSystem
其他操作:
removeExtension/indexOfExtension
separatorsToSystem/separatorsToUnix/separatorsToWindows
indexOfLastSeparator
IOUtils 流操作工具类
读操作:lineIterator/read/readLines
写操作:write/writeLines
转换: toInputStream/toBufferedInputStream/toByteArray/toCharArray/toString
其他操作:copy/copyLarge/contentEquals/skip/skipFully/closeQuietly
文件比较器:
CompositeFileComparator/DefaultFileComparator/DirectoryFileComparator
ExtensionFileComparator/LastModifiedFileComparator/NameFileComparator
PathFileComparator/PathFileComparator
文件过滤器:
AgeFileFilter/AndFileFilter/CanReadFileFilter/CanWriteFileFilter
DelegateFileFilter/DirectoryFileFilter/EmptyFileFilter/FalseFileFilter/FileFileFilter
FileFilterUtils/HiddenFileFilter/MagicNumberFileFilter/NameFileFilter/NotFileFilter
OrFileFilter/PrefixFileFilter/RegexFileFilter/SizeFileFilter/SuffixFileFilter
TrueFileFilter/WildcardFileFilter/WildcardFilter
3.1.2. common-lang3
StringUtils:
包含判断方法:contains/containsXXX
字符串替换方法:replace/replaceXXX
获取子串:substring/substringXXX
判断方法:
1、isEmpty/isNotEmpty/isBlank/isNotBlank/isNumeric/isWhitespace
2、sartsWith/startsWithAny/endsWith/endsWithIgnoreCase
索引(index):indexOf/indexOfXXX/tIndexOf/lastIndexOfXXX
处理方法:
abbreviate 缩短 capitalise 首字母 repeat 重复 left/right/center 左右中间
removeXXX 移除 trimXXX 去空 reverseXXX 翻转 stripXXX 移除
defaultXXX 默认 lowerCase/upperCase deleteXXX 删除处理
splitXXX分解处理 join 拼接
StringEscapeUtils 转义字符串工具类
对html js xml sql 等代码进行转义来防止注入攻击
escapeCsv/unescapeCsv/escapeHtml/unescapeHtml/escapeJava/unescapeJava
escapeJavaScript/unescapeJavaScript/escapeXml/unescapeXml/escapeSql
NumberUtils 数字工具类
判断是否数字:isDigits/isNumber
其他方法:compare,max,min,
ArrayUtils 数组工具类
添加移除:add,addAll,remove,removeElement,
拷贝:clone
判断:contains,isEmpty,isNotEmpty,isEquals,isSameLength,
其他:getLength,indexOf,lastIndexOf,nullToEmpty,reverse,subArray,
转换:toMap,toObject,toPrimitive,toString
RandomUtils 随机数工具类
nextBoolean/nextInt/nextLong/nextFloat/nextDouble
EnumUtils 枚举工具类
getEnum/getEnumIgnoreCase/getEnumList/getEnumMap
iterator
ClassUtils 类工具
获取:
1、类和接口 :getClass/getAllInterfaces/getAllSuperclasses/getShortClassName
2、包:getPackageName/getPackageCanonicalName
3、方法:getPublicMethod
转换:
1、toClass/convertClassesToClassNames/convertClassNamesToClasses/
2、primitivesToWrappers/primitiveToWrapper/wrappersToPrimitives/wrapperToPrimitive
判断:isAssignable/isInnerClass
MethodUtils
getAccessibleMethod/getMatchingAccessibleMethod
invokeMethod/invokeStaticMethod/invokeExactMethod/invokeExactStaticMethod
FieldUtils
getField/readField/writeField
getDeclaredField/readDeclaredField/writeDeclaredField
readDeclaredStaticField/readStaticField/writeDeclaredStaticField/writeStaticField
ConstructorUtils
getAccessibleConstructor/getMatchingAccessibleConstructor
invokeConstructor/invokeExactConstructor
ObjectUtils 对象工具类
max/min/toString/identityToString/appendIdentityToString/defaultIfNull
SystemUtils 系统属性工具类
getJavaHome/getJavaIoTmpDir/getJavaVersion/getUserDir/getUserHome/
isJavaAwtHeadless/isJavaVersionAtLeast
LocaleUtils 本地工具类
availableLocaleList/availableLocaleSet
countriesByLanguage
localeLookupList/toLocale/isAvailableLocale/languagesByCountry
3.1.3. commons-collections4
CollectionUtils 集合工具类
添加/删除:addAll/addIgnoreNull/retainAll/removeAll/
获取:
find/get/containsAny/index/size/sizeIsEmpty/select/selectRejected/subtract
typedCollection
判断:
isEmpty/isNotEmpty/isFull/exists/isEqualCollection/
isSubCollection/isProperSubCollection
转换:
collect/transform/transformedCollection/predicatedCollection
unmodifiableCollection/synchronizedCollection
计算:cardinality/countMatches/maxSize
过滤:filter
集合:intersection/union/disjunction 交集,并集,差集
其他操作:
reverseArray 翻转 forAllDo 给每个元素执行闭包
getCardinalityMap 转成Map,key是元素,value是次数
3.1.4. Commons FileUpload
为Web应用程序或Servlet提供文件上传功能
3.1.5. Commons Codec
提供常用的编码和解码方法,如DES、SHA1、MD5、Base64、URL和Soundx等。
3.1.6. Commons Compress
是一个压缩、解压缩文件的组件,可以操作rar、cpio、Unix dump、tar、zip、gzip、XZ、Pack200和bzip2格式的压缩文件。
3.1.7. Commons Configuration
可以从properties或者xml文件中加载配置信息。
3.1.8. Commons Daemon
实现将普通的Java应用变成系统的后台服务,例如 Tomcat 就是利用这个项目来实现作为 Linux 和 Windows 的服务启动和停止的。
3.1.9. Commons Exec
用来执行外部进程,如执行exe文件或命令行
3.1.10. Commons Net
封装了各种网络协议的客户端,支持FTP、NNTP、SMTP、POP3、Telnet等协议。
3.2. Google guava
3.2.1. 集合工具类
普通集合
List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList();
Set<String> set = Sets.newHashSet();
Map<String, String> map = Maps.newHashMap();
不可变集合(immutable)
ImmutableList<Integer> iList = ImmutableList.of(12,54,87);
ImmutableSet<Integer> iSet = ImmutableSet.of(354,54,764,354);
ImmutableMap<String, Integer> iMap = ImmutableMap.of("k1", 453, "k2", 534);
Set 取交集、并集、差集
map 取交集、并集、差集也是类似
Sets.union(setA, setB);
Sets.difference(setA, setB);
Sets.intersection(setA, setB);
MultiSet: 无序+可重复
Multimap :key 可以重复的 map
BiMap:双向 Map (Bidirectional Map) 键与值都不能重复 (这个稍稍正常一点。如果 key 重复了则会覆盖 key ,如果 value 重复了则会报错。)
连接符(Joiner)和分隔符(Splitter)#
String result = Joiner.skipNulls().on("-").join(list);
String result = Joiner.on(",").withKeyValueSeparator("=").join(map);
Map<String,String> map = Splitter.on(",").withKeyValueSeparator("=").split(str);
List<String> list = Splitter.on("-").splitToList(str);
构造比较器
Comparator 的实现#
Ordering<UserInfo> byOrdering = Ordering.natural().nullsFirst().onResultOf((Function<UserInfo, Comparable<Integer>>) input -> input.getGender());
System.out.println(byOrdering.compare(build1, build));
3.2.2. Guava Cache
// LoadingCache是Cache的缓存实现
LoadingCache<String, Object> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
//设置缓存大小
.maximumSize(1000)
//设置到期时间
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
//设置缓存里的值两分钟刷新一次
.refreshAfterWrite(2, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
//开启缓存的统计功能
.recordStats()
//构建缓存
.build(new CacheLoader<String, Object>() {
//此处实现如果根据key找不到value需要去如何获取
@Override
public Object load(String s) throws Exception {
return new Object();
}
//如果批量加载有比反复调用load更优的方法则重写这个方法
@Override
public Map<String, Object> loadAll(Iterable<? extends String> keys) throws Exception {
return super.loadAll(keys);
}
});
cache.invalidateAll();//清除所有缓存项
//清理的时机:在写操作时顺带做少量的维护工作,或者偶尔在读操作时做——如果写操作实在太少的话
//如果想自己维护则可以调用Cache.cleanUp();
cache.cleanUp();
//另外有时候需要缓存中的数据做出变化重载一次,这个过程可以异步执行
cache.refresh("key");
3.2.3. 单机限流工具类 - RateLimiter#
漏桶算法:
- 像一个漏斗一样,水一滴一滴的滴下去,流出是匀速的。
- 漏桶算法的实现依赖队列,一个处理器从队头依照固定频率取出数据进行处理
- 当访问量过大的时候这个漏斗就会积水, 如果请求量过大导致队列堆满那么新来的请求就会被抛弃
令牌桶:
- 令牌桶取出令牌的速度没限制,只要有令牌就能处理。所以令牌桶允许一定程度的突发,而漏桶主要目的是平滑流出。
- 初始给桶中添加固定容量令牌,当桶中令牌不够取出的时候则拒绝新的请求。
RateLimiter 使用了令牌桶算法,提供两种限流的实现方案:
平滑突发限流(SmoothBursty)
RateLimiter r = RateLimiter.create(5); // 每秒放置的令牌数为 5 个
while (true) {
System.out.println("get 1 tokens: " + r.acquire() + "s");
}
//输出:
//基本 0.2s 一次符合每秒 5 个的设置。保证每秒不超过 5 个达到了平滑输出的效果
get 1 tokens: 0.0s
get 1 tokens: 0.197059s
get 1 tokens: 0.195338s
get 1 tokens: 0.196918s
平滑预热限流(SmoothWarmingUp)
3.3. spring utils
3.3.1. bean 复制 克隆
beancopier
https://github.com/mapstruct/mapstruct
3.3.2. 字符串
// >>> springboot 自带
RandomStringUtils 生成随机字符串, 随机数字
StringUtils.isEmpty() 并非严格的空
3.3.3. 编解码
// >>> springboot 自带
public static String getMD5(String str) {
String base = str + "/" + salt;
String md5 = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(base.getBytes());
return md5;
}
4. 和 react 一起打包
https://github.com/arpan-banerjee7/demo-spring-react-maven-plugin
TODO
5. Spring Boot中的注解
5.1. @ConfigurationProperties 和 @Value
基本使用-注入值
@Value 是core container的feature。不支持宽松绑定,不支持Meta-data。但支持spELl。
@ConfigurationProperties 则支持宽松绑定,支持Meta-data。但不支持spELl。
@ConfigurationProperties一般只用来处理环境信息,不用来注入自定义属性(这段不知道翻译得准不准,原文如下:Even if the configuration above will create a regular bean for FooProperties, we recommend that @ConfigurationProperties only deal with the environment and in particular does not inject other beans from the context. Having said that, The @EnableConfigurationProperties annotation is also automatically applied to your project so that any existing bean annotated with @ConfigurationProperties will be configured from the Environment.)
配置文件:
myProps: #自定义的属性和值
simpleProp: simplePropValue
arrayProps: 1,2,3,4,5
listProp1:
- name: abc
value: abcValue
- name: efg
value: efgValue
listProp2:
- config2Value1
- config2Vavlue2
mapProps:
key1: value1
key2: value2
创建一个bean来接受信息:(这里不推荐这么用, 应该使用 @value 老老实实属性写全)
// @Component // 这个注解可选
@data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="myProps") //接收application.yml中的myProps下面的属性 (prefix 必须, 不可为"", 需要在配置类中 enable config props class)
// 此时 idea 提示 spring boot config annotation processor not configured, 是因为他以为你要为配置文件指定自定义属性, 需要生成提示
// 可以https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.3.4.RELEASE/reference/html/appendix-configuration-metadata.html#configuration-metadata-annotation-processor
public class MyProps {
private String simpleProp;
private String[] arrayProps;
private List<Map<String, String>> listProp1 = new ArrayList<>(); //接收prop1里面的属性值
private List<String> listProp2 = new ArrayList<>(); //接收prop2里面的属性值
private Map<String, String> mapProps = new HashMap<>(); //接收prop1里面的属性值
}
ConfigurationProperties 和 Bean 配合使用
除了可以使用@ConfigurationProperties注解一个类,还可以在@Bean方法上使用;需要绑定属性到不受你控制的第三方组件时,这种方式非常有用。
// 为了从环境属性配置一个bean,将@ConfigurationProperties添加到它的bean注册过程,任何以foo为前缀的属性定义都会被映射到FooComponent上:
//
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "foo")
@Bean
public FooComponent fooComponent() {
...
}
// DataSource 是第三方类库, 如下绑定值就非常方便
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="spring.datasource")
public DataSource druid() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
对于无法转换的属性, 比如本来是一个 Boolean 类型, 但是配置文件中配置的是 string 类型, ignoreInvalidFields 可以决定是否抛出异常, 默认为 false, 表示要抛出异常
对于配置文件中多余的属性, ignoreUnknownFields 决定是否抛出异常, 默认 true, 表示不抛出异常
5.2. @EnableConfigurationProperties
配置哪些类是用来接受配置文件信息的bean,当@EnableConfigurationProperties注解应用到你的@Configuration时,任何被@ConfigurationProperties注解的beans将自动被Environment属性配置 , configBean 无需 @component
@EnableConfigurationProperties({LiquibaseProperties.class, ApplicationProperties.class})
当一个 @ConfigurationProperties bean 像如上这样注册,这个bean就有了一个名字,规范是这样:<prefix>-<fqn>, 即:前缀-全限定名,如:
myProps-com.xy.PropertiesBean
enableXXX 类注解原理就是 定义一个注解, 在注解上通过 @import 引入一个配置类
5.3. @EnableAutoConfiguration
根据添加的jar依赖猜测你想如何配置Spring,如果发现应用了你不想要的特定自动配置类,你可以使用 @EnableAutoConfiguration 注解的exclude属性来禁用它们
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {MetricFilterAutoConfiguration.class, MetricRepositoryAutoConfiguration.class})
使用一般是@EnableAutoConfiguration加到一个主@configration类上,主配置类一般就是app的启动类
5.4. @ComponentScan
扫描所有Spring组件,通过@autowired注入使用
如果使用上面建议的结构组织代码(将应用类放到根包下),你可以添加 @ComponentScan 注解而不需要任何参数。你的所有应用程序组件( @Component , @Service , @Repository , @Controller 等)将被自动注册为Spring Beans。
5.5. @SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication 注解等价于以默认属性使用 @Configuration , @EnableAutoConfiguration 和 @ComponentScan
5.6. @Component和@Bean和@Configration区别
@Configuration 注解本质上还是 @Component,
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;// 默认为 true, config bean 中的方法被 cglib 代理, 表示 在同个 config bean 中嵌套调用方法, 返回的对象默认从 ioc container 中获取, 不会新创建对象
}
@Configuration一般和@bean合用, @component和@bean不能合用
Spring Boot提倡基于Java的配置,通常简易启动类作为主配置类,其他配置类通过@import导入到主配置类;@ComponentScan也会扫描配置类 ,如果不得不使用基于xml的配置,仍旧可以从一个@configration类开始,通过@ImportResource 注解加载XML配置文件。
@Component被用在要被自动扫描和装配的类上,Spring 注解@Component等效于@Service,@Controller,@Repository;@Bean只能用于方法(方法名作为ioc容器中的bean name)和注解上。用@Configuration注解该类,等价 与XML中配置beans;用@Bean标注方法等价于XML中配置bean。
在项目中,本工程的bean注册,使用@Component,通过web service取得的bean,通过@Bean标注在获取方法上注册;
5.7. @Import和@ImportResource和@PropertySource比较
- 前两者都需要和@configuration配合使用(Both @Import @ImportResource work with @Configuration), 表示导入额外的配置
- @import 导入某个配置类, 这个配置类可以不用标注 @configuration (一般会配合自定义注解使用: 自定义注解上通过 @import 导入多个未标注@configuration 的配置类使得这些配置类生效)
- @ImportResource用来引入外置的配置文件, 如@ImportResource({"classpath:datasource.xml"}), 一般用来导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面功能生效
- @Import引入另外的@configuration类
- @PropertySource用于加载另外的属性配置文件, 如@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"}), 一般和@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")一起用 springboot默认只会加载application.properties中的属性,
例子:
@Configuration
@Import(AnotherConfig.class)
@ImportResource(“classpath:/com/acme/properties-config.xml”)
@PropertySource(“classpath:some.properties”)
public class AppConfig
{
// blah…
}
6. 常用扩展点
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor
Import
Aware回调
InitlizingBean
FactoryBean
SmartInitlizingSingleton
ApplicationListener -- event事件
Lifecycle 容器启动,停止回调
HandlerInterceptor 请求处理前后统计,计算.
7. context 上下文 手动注册bean
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36628536/article/details/113753368 介绍
// plan 1: (此种方式注册的bean在调用时将由spring进行创建,相当于延迟加载bean)
@Component
public class ApplicationContextUtil implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
applicationContext=context;
}
/**
* 动态注入bean
* @param requiredType 注入类
* @param beanName bean名称
*/
public static Object registerBean(Class<?> requiredType,String beanName){
//将applicationContext转换为ConfigurableApplicationContext
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext;
//获取BeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) configurableApplicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory();
//创建bean信息.
BeanDefinitionBuilder beanDefinitionBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(requiredType);
//动态注册bean.
defaultListableBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinitionBuilder.getBeanDefinition());
//获取动态注册的bean.
return configurableApplicationContext.getBean(requiredType);
}
}
// plan 2: (此种方式允许手动创建单例bean实例并注册,注意必须是单例的,在spring调用时,会将手动创建的bean直接注入到调用方)
@Component
public class ApplicationContextUtil implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
applicationContext=context;
}
/**
* 动态注入单例bean实例
* @param beanName bean名称
* @param singletonObject 单例bean实例
* @return 注入实例
*/
public static Object registerSingletonBean(String beanName,Object singletonObject){
//将applicationContext转换为ConfigurableApplicationContext
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext;
//获取BeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) configurableApplicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory();
//动态注册bean.
defaultListableBeanFactory.registerSingleton(beanName,singletonObject);
//获取动态注册的bean.
return configurableApplicationContext.getBean(beanName);
}
}
8. 实现事件驱动
/*
ApplicationEvent:表示事件本身,自定义事件需要继承该类,用来定义事件
ApplicationEventPublisher:事件发送器,主要用来发布事件
ApplicationListener:事件监听器接口,监听类实现ApplicationListener 里onApplicationEvent方法即可,也可以在方法上增加@EventListener以实现事件监听。
*/
// 默认情况下事件是同步的。即事件被publish后会等待Listener的处理。如果发布事件处的业务存在事务,监听器处理也会在相同的事务中。如果需要异步处理事件,可以onApplicationEvent方法上加@Aync支持异步或在有@EventListener的注解方法上加上@Aync
public class ProductEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public ProductEvent(Product product) {
super(product);
}
}
@Service
public class ProductServiceImpl implements IproductService {
...
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void saveProduct(Product product) {
productMapper.saveProduct(product);
//事件发布
publisher.publishEvent(product);
}
...
}
@Slf4j
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ProductListener {
private final NotifyService notifyServcie;
@Async // 需要@EnableAsync
@Order
@EventListener(ProductEvent.class)
public void notify(ProductEvent event) {
Product product = (Product) event.getSource();
notifyServcie.notify(product, "product");
}
}
// 等效 @eventListner
@Component
public class RegisterListener implements ApplicationListener<UserRegisterEvent>
{
/**
* 实现监听
* @param userRegisterEvent
*/
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(UserRegisterEvent userRegisterEvent) {
//获取注册用户对象
UserBean user = userRegisterEvent.getUser();
//../省略逻辑
//输出注册用户信息
System.out.println("注册信息,用户名:"+user.getName()+",密码:"+user.getPassword());
}
}
9. 优雅停机 关机
,1、利用底层JVM Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook() 添加自己的钩子函数。
2、利用Spring 现有机制,Spring会在关机时发送ContextClosedEvent给到监听器,我们只需要把关闭函数放在监听器里即可。
优雅关机的过程应该是通知注册中心->暂停接收新请求->旧请求执行完毕->其余的清理动作
// 这里采用方式 2:
// 监听器
private static class GracefulShutdown implements TomcatConnectorCustomizer,
ApplicationListener<ContextClosedEvent>, Ordered {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GracefulShutdown.class);
private volatile Connector connector;
/**
* 控制GracefulShutdown listener优先级是最高的
*/
private int order = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE;
@Override
public void customize(Connector connector) {
this.connector = connector;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextClosedEvent event) {
logger.info("eureka client shutting down");
eurekaClient.shutdown();
logger.info("Completed shut down eureka client");
// Tomcat暂停接收request
this.connector.pause();
logger.info("connector pause");
// 关闭Tomcat线程池
Executor executor = this.connector.getProtocolHandler().getExecutor();
if (executor instanceof ThreadPoolExecutor) {
try {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = (ThreadPoolExecutor) executor;
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
logger.info("connector executor shutting down");
if (!threadPoolExecutor.awaitTermination(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
logger.warn("Tomcat thread pool did not shut down gracefully within "
+ "10 seconds. Proceeding with forceful shutdown");
}
logger.info("completed shut down connector executor");
}
catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return this.order;
}
}
// springboot 配置
/**
* 用于优雅关闭tomcat
*/
@Bean
public GracefulShutdown gracefulShutdown(EurekaClient eurekaClient) {
return new GracefulShutdown(eurekaClient);
}
/**
* 用于优雅关闭tomcat
*/
@Bean
public WebServerFactoryCustomizer tomcatCustomizer(GracefulShutdown gracefulShutdown) {
return factory -> {
if (factory instanceof TomcatServletWebServerFactory) {
((TomcatServletWebServerFactory) factory)
.addConnectorCustomizers(gracefulShutdown);
}
};
}
10. 静态注入
为静态属性注入值, 使用通过 XXXClass.xxx 使用
10.1. set注入
@Component(value = "MongoConfig")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mongo.config")
public class MongoConfig {
private static String chat_username;
@Value("${mongo.config.username}")
public void setChat_username(String chat_username) {
MongoConfig.chat_username = chat_username;
}
}
10.2. @PostConstruct 注入
@Component
public class ADUserUtils {
@Resource
private ADConfig adc;
private static ADConfig adc1;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
this.adc1 = adc;
}
public static List<User> getADUsers() {
adc1.readConf();
}
10.3. 通过 ApplicationContext
得到静态的 context, 然后通过 getBean(xxx.class) ...
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan({"io.github.xiaoyureed.mockitomybatisplusdemo.mapper"})
public class MockitoDemoApplication {
private static ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
public static void main(String[] args) {
context = SpringApplication.run(MockitoDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
11. 使用starter
servlet request wrapper
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43935907/article/details/98476935 https://www.cnblogs.com/JAYIT/p/10943155.html https://www.cnblogs.com/exmyth/p/10332328.html
11.1. 加载过程or原理
@SpringBootApplication包含了@EnableAutoConfiguration,这个注解又包含@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)。
spring boot启动时,会调用AutoConfigurationImportSelector的回调函数,让其解析所有包下的"META-INF/spring.factories" (位于项目结构的 resources/META-INF/spring.factories 下), 并把key为"...EnableAutoConfiguration"对应的value里的类都加载为Bean,而那些类基本都是注解了@Configuration的配置类。这便是spring boot能自动配置的原因。
11.2. 自动配置类会用到的一些注解
https://my.oschina.net/u/566591/blog/2250290
@Configuration 表明是一个配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class}) 使用starter的时候排除自动配置
@ConditionalOnClass 当classpath下发现该类的情况下进行自动配置 (name, value 任选其一)
@ConditionalOnMissingClass 没有这个类时应用标注的配置类
@ConditionOnMissingBean 在spring容器中没找到 bean 时 (如果不指定, 默认 方法返回值类型/当前类)
@ConditionalOnBean 当容器中有指定的Bean的条件下
# 默认是检查bean的类型, 看看容器中是否有同类型 bean 存在, 不看 bean name;
# 开启按照 bean name 检查: 属性 name = {xxx"}
# @ConditionalOnBean(name = {"hah", "hoo"}): "and" 关系, 有 hah, 且有 hoo, return true. 任何一个缺失都return false
# @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = {"hah", "hoo"}): "and " 关系, 没hah 且 没 hoo, return true. 任何一个出现, return false
@EnableConfigurationProperties(XxxProperties.class) 使 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="aaa.bbb") 注解生效
@ConditionalOnProperty:指定的属性有指定的值时
# ConditionalOnProperty
name/value (value 用于指定某配置一定要出现), havingValue 指定配置文件中的属性, 为 null返回 false, 不匹配返回false
matchIfMissing 配置项如果缺失, 是否匹配, 默认 false
# 优先级比 onBean, onClass 这些都高
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate: (和 @ConditionalOnBean 类似)当指定的Bean在容器中只有一个,或者在有多个Bean的情况下,用来指定首选的Bean
@ConditionalOnExpression:基于SpEL表达式作为判断条件
@ConditionalOnResource(resources = {"/xxx.yml"}):类路径下是否有指定的资源
@ConditionalOnJava(javaversion.eight):基于JVM/Java版本作为判断条件
@ConditionalOnJndi:在JNDI存在的条件下查找指定的位置, 必须存在一个.否则,返回不匹配
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication:当前项目不是Web项目的条件下
@ConditionalOnWebApplication:当前项目是Web项目的条件下
@AutoConfigureAfter(A.class) 配置类将在 A.class 之后加载
@AutoConfigureBefore ... 之前加载
@AutoConfigureOrder
11.3. 自动配置类的实例
11.3.1. spring 动态代理
https://lolico.me/2020/05/03/SpringBoot2-AOP-uses-cglib-proxy-by-default/
//SpringBoot1.5.x中的这个自动配置类会发现默认是使用jdk动态代理,那么为什么在SpringBoot2.x中改为默认使用Cglib了
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public class AopAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(Advice.class)
static class AspectJAutoProxyingConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "false",
matchIfMissing = false)
static class jdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true) // 能够看出AOP默认使用Cglib代理
static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
}
// ...
}
11.4. @Conditional
自动配置相关注解底层都是通过 @Conditional(OnClassCondition.class) 实现的
通过它, 可以自己定制条件
https://my.oschina.net/u/566591/blog/2250290
11.5. 封装组合条件
继承 AllNestedConditions 封装多条件 (and 关系)
AnyNestedCondition (or 关系)
NoneNestedConditions (none 关系)
11.6. 创建自己的 starter
创建一个starter 项目
命名规则: spring boot 官方 starter 命名为 "spring-boot-starter-xxx", 自定义的starter 命名 "xxx-spring-boot-starter";
引入
spring-boot-configuration-processor(编译时生成 spring-configuration-metadata.json ,在IDE中编辑配置文件时,会出现提示), 标注为 optional: true 避免依赖传递引入
spring boot starter(相关注解需要), 标注为 optional true, idea 中 spring boot app 创建时自动导入了继承
spring-boot-starter-parent, 如果想不通过继承方式使用, 可以 dependencyManagementspring boot dependencies, 参考 但是这种方式有个弊端, 就是需要指定 spring-boot-maven-plugin 的 goal, 如果用 parent 的方式则不需要这一点<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>如果是生成的 spring boot 项目, 删除 启动类, 然后替换 spring boot maven 插件 为
maven-compile-plugin(因为没有启动类, repackage 会报错), 设置 properties 下 maven.compiler.source, maven.compiler.target, java.version创建一个 @ConfigurationProperties 类用于保存你的配置信息, 在 @EnableConfigurationProperties(...) 类上指定, (或者标注 component 然后配置componentScan 或者直接 @configurationPropertiesScan)
(如果你的项目不使用配置信息则可以跳过这一步,不过这种情况非常少见)
创建一个AutoConfiguration,引用定义好的配置信息;在AutoConfiguration中实现所有starter应该完成的操作,并且把这个类加入classpath:/META-INF/spring.factories配置文件中进行声明
自动配置类不应启用组件扫描以查找其他组件 (即 若生成的是spring boot 骨架, 应去掉启动类)。应该使用 @import 来导入其他配置类
打包发布
如果 starter 就是本地自己使用, 可以不打包不发布, 直接在另外的项目中引入
spring.factories 示例:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration = \
com.mycorp.libx.autoconfigure.LibXAutoConfiguration,\
com.mycorp.libx.autoconfigure.LibXWebAutoConfiguration
11.7. 反爬虫 starter
https://www.cnblogs.com/zouhao/p/12175653.html
TODO
11.8. gprc starter
https://github.com/yidongnan/grpc-spring-boot-starter
12. 监控 and 安全
密码加密 Argon2
Spring Vault,它为HashiCorp Vault添加抽象 -> 密码存储
OWASP ZAP 渗透测试报告
12.1. spring-boot-actuator 监控
https://www.cnblogs.com/zwqh/p/11851300.html https://www.jianshu.com/p/8bfac9289c7e
spring boot 的 sub project, 提供产品级别的监控
spring cloud 中, refresh 的 post 端点被 actuator 接管, 配置 management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=health,info (默认) 需要添加 'refresh', 最终需要 curl -d{} http://xxx:xxx/actuator/refresh
hystrix.stream 也被接管, 配置添加 'hystrix.stream', 监控流为 http://xxx:xxx/actuator/hystrix.stream
自己写监控, 可以:
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(PaymentServiceApp.class, args);
ConfigurableEnvironment env = context.getEnvironment();
// 或者 直接 @autowired Environment env
ui展示: https://github.com/codecentric/spring-boot-admin
12.2. spring boot admin 监控界面
https://www.jianshu.com/p/483adafc6b3a //todo
12.3. spring-boot-starter-security
12.3.1. security组件介绍
[ref]](https://www.cnblogs.com/demingblog/p/10874753.html)
spring security 是安全认证框架, 基于 Servlet filter, 核心就是一组过滤器链; 可在 Web 请求级和方法调用级处理身份确认和授权
如果是 普通的 spring 项目, 使用 shiro 更简单
================================= 核心组件
SecurityContext - 用户 auth 通过后, authentication 信息存储在这里, 可以在任意地方使用 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().set/getAuthentication
SecurityContextHolder - 在任意地方可以获取 SecurityContext
Authentication - 认证信息对象, 表示认证后的用户
UserDetails - 认证用户的详细信息
UserDetailsService - 可以用来获取UserDetails。我们会自定义一个CustomUserDetailsService来实现UserDetailsService接口, 通过 username 查询到 userDetails, 如果没查到 , UsernameNotFoundException
AuthenticationManager - 作用就是校验Authentication, 校验失败抛出 BadCredentialsException
12.3.2. 基本使用 和 配置用户名密码
配合 starter (spring-boot-starter-security), 可以零配置使用. 引入后依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
如下配置即可
server:
port: 8000
spring:
application:
name: spring-security-demo
security:
user:
# 如果不配置, 默认为 user/控制台日志中看到默认密码
# 前端调用, 需要 basic auth 认证
name: root
password: root
支持两种验证方式:
可以通过 form 表单来认证 (默认)
适合页面验证
可以通过 HttpBasic 来认证 (basic auth)
适合 api 接口的验证, 当然也适合页面
用户名密码也可以在这里:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
@Override
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
UserDetails user =
User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username("user")
.password("password")
.roles("USER")
.build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user);
}
}
12.3.3. 禁用基本认证
如果既想使用security又不想每次输入用户名密码,可以直接在Application文件中禁用自动配置 (方法 1)
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration.class
})
或者 在代码中配置 (方法 2)
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
是因为覆盖了父类方法, 父类中的方法内容如下:
http.authorizeRequests((requests) -> requests.anyRequest().authenticated()); // 所有 请求都需要认证
http.formLogin(); // 支持表单认证
http.httpBasic(); // 支持 basic auth 认证
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 这里为空, 表示无需 任何认证
// super.configure(http);
}
}
12.3.4. 配置中 WebSecurity 和 HttpSecurity 区别
// - WebSecurity:用于配置一些与 Servlet 容器相关的安全性设置,如忽略某些 资源的权限校验等。
// WebSecurity 的配置通常较简单,主要还是 HttpSecurity 负责了绝大部分的认证与授权功能配置。所以,总体来说,WebSecurity 配置微调,HttpSecurity 配置主体
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web
.ignoring()
.antMatchers("/resources/**") // 忽略
.antMatchers("/publics/**"); // 忽略
}
// - HttpSecurity:用于配置与 HTTP 请求路由相关的权限控制和认证设置,如表单登录,HTTP 基础认证,访问控制等。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/publics/**").hasRole("USER") // no effect, 因为 WebSecurity 中配置了 忽略 publics/** 下的验证
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin().loginPage("/login").permitAll()
.and()
.logout().permitAll();
}
================================ 实现方法级别的权限控制
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled =true) 使用表达式实现方法级别的安全性 , 4个注解可用
@PreAuthorize 在方法调用之前,基于表达式的计算结果来限制对方法的访问
@PostAuthorize 允许方法调用,但是如果表达式计算结果为false,将抛出一个安全性异常
@PostFilter 允许方法调用,但必须按照表达式来过滤方法的结果
@PreFilter 允许方法调用,但必须在进入方法之前过滤输入值
//表示如果用户具有admin角色,就能访问listAllUsers方法,如果方法前不加@preAuthorize注解,意味着所有用户都能访问listAllUsers
@PreAuthorize("hasRole(‘admin‘)")
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
publicList listAllUsers() {
……
}
此外还有 :
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled=true) 开启@Secured 注解过滤权限
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(jsr250Enabled=true)开启@RolesAllowed 注解过滤权限
12.3.5. 配置跨域
https://lolico.me/2020/04/26/Spring-Security-CORS/ TODO
12.4. oauth2
spring security oauth2
check outline-about-authentication-oauth2.md
13. 日志
13.1. Log4j2-Marker 写入到指定日志文件
https://www.jianshu.com/p/1ff824bc997a?utm_campaign
13.2. logback
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<!--应用名称-->
<property name="APPLICATION_NAME" value="roncoo-pay-app-notify"/>
<!-- 文件输出格式 -->
<property name="PATTERN" value="%-12(%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS}) |-%-5level [%thread] %c [%L] -| %msg%n"/>
<!-- 文件路径 -->
<property name="FILE_PATH" value="/home/roncoo/opensource/pay/logs"/>
<!-- 控制台 -->
<appender name="CONSOLE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>${PATTERN}</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!--日志文件策略-->
<appender name="LOGGER_FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${FILE_PATH}/${APPLICATION_NAME}/${APPLICATION_NAME}.log</file>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>${FILE_PATH}/${APPLICATION_NAME}/${APPLICATION_NAME}.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log
</fileNamePattern>
<MaxHistory>100</MaxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<pattern>${PATTERN}</pattern>
</layout>
</appender>
<logger name="com.roncoo.pay" level="debug"/>
<!-- LOG "com.baeldung*" at TRACE level -->
<logger name="com.baeldung" level="trace" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="RollingFile" />
<appender-ref ref="Console" />
</logger>
<!-- 所有日志都打印 info 级别 -->
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE"/>
<appender-ref ref="LOGGER_FILE"/>
</root>
</configuration>
14. cqrs模式
类似 "读写分离"
# Spring Boot CQRS(Command Query Responsibility Segregation)和事件溯源(Event Sourcing)是两个相对独立的技术概念,但在实际应用中通常会一起使用
命令查询职责分离 (Command Query Responsibility Separation,CQrS) : 一种软件架构模式,将系统的写入操作和读取操作分离开来。在CQRS模式中,所有的写入操作都由命令(Command)对象处理,而所有的读取操作都由查询(Query)对象处理。这种分离使得系统更容易扩展,更容易处理高并发的读写操作
命令(Command):不返回任何结果(void),但会改变对象的状态。
查询(Query):返回结果,但是不会改变对象的状态,对系统没有副作用。
事件溯源(Event Sourcing): 是一种用于记录系统状态变化的方法。在事件溯源模式中,系统的每一个状态变化都被记录为一个事件(Event),并且这些事件是不可变的。通过对事件的回放,可以还原出系统的任何一个历史状态。
15. 数据层
集成 elasticSearch es
基于 spring boot data
<!-- 这个依赖会包含Elasticsearch的Java API和Spring Data Elasticsearch模块。Spring Data Elasticsearch模块提供了一组实用的工具和方法来简化数据访问层的开发 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring:
data:
elasticsearch:
cluster-name: my-cluster-name
cluster-nodes: 127.0.0.1:9300
// 通过ElasticsearchRepository提供的方法,我们可以轻松实现索引的增删改查操作
public interface ArticleRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Article, Long> {
}
// specify the index name (db name) and doc type(table name)
@Document(indexName = "article_index", type = "article")
public class Article {
@Id
private Long id;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text, analyzer = "ik_max_word")
private String title;
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String author;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text, analyzer = "ik_max_word")
private String content;
@Field(type = FieldType.Date, format = DateFormat.custom, pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
private Date createTime;
// 省略getter/setter方法
}
// save data
articleRepository.save(article);
// delete
articleRepository.deleteById(1L);
// update
Optional<Article> optional = articleRepository.findById(1L);
if (optional.isPresent()) {
Article article = optional.get();
article.setContent("Spring Data Elasticsearch is powerful.");
articleRepository.save(article);
}
// query by id
Optional<Article> optional = articleRepository.findById(1L);
// 根据关键词查询数据
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(0, 10);
String keyword = "easy";
HighlightBuilder.Field titleField = new HighlightBuilder.Field("title")
.preTags("<em>").postTags("</em>");
SearchQuery searchQuery = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder()
// NativeSearchQueryBuilder提供了丰富的方法来构建各种查询语句,例如termQuery、rangeQuery、boolQuery等
.withQuery(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title", keyword))
.withPageable(pageable)
// 高亮显示搜索结果
.withHighlightFields(titleField);
// 使用过滤器筛选数据
.withFilter(FilterBuilders.termFilter("author", "binjie09"))
.build();
Page<Article> articlePage = articleRepository.search(searchQuery);
List<Article> articleList = articlePage.getContent();
for (Article article : articleList) {
String title = article.getTitle();
if (article.getHighlights().size() > 0) {
title = article.getHighlights().get(0).getFragments()[0].toString();
}
System.out.println(title);
}
基于原生 es 客户端
<!-- ES 客户端 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>${elasticsearch.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- ES 版本 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>${elasticsearch.version}</version>
</dependency>
@Configuration
public class ESConfig {
@Value("${yunshangxue.elasticsearch.hostlist}")
private String hostlist; // 127.0.0.1:9200
@Bean // 高版本客户端
public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient() {
// 解析 hostlist 配置信息。假如以后有多个,则需要用 , 分开
String[] split = hostlist.split(",");
// 创建 HttpHost 数组,其中存放es主机和端口的配置信息
HttpHost[] httpHostArray = new HttpHost[split.length];
for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) {
String item = split[i];
httpHostArray[i] = new HttpHost(item.split(":")[0], Integer.parseInt(item.split(":")[1]), "http");
}
// 创建RestHighLevelClient客户端
return new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(httpHostArray));
}
// 项目主要使用 RestHighLevelClient,对于低级的客户端暂时不用
@Bean
public RestClient restClient() {
// 解析hostlist配置信息
String[] split = hostlist.split(",");
// 创建HttpHost数组,其中存放es主机和端口的配置信息
HttpHost[] httpHostArray = new HttpHost[split.length];
for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) {
String item = split[i];
httpHostArray[i] = new HttpHost(item.split(":")[0], Integer.parseInt(item.split(":")[1]), "http");
}
return RestClient.builder(httpHostArray).build();
}
}
// 删除索引
// 操作索引的对象
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
// 删除索引的请求
DeleteIndexRequest deleteIndexRequest = new DeleteIndexRequest("ysx_course");
// 删除索引
DeleteIndexResponse response = indices.delete(deleteIndexRequest);
// 得到响应
boolean b = response.isAcknowledged()
// 创建
// 操作索引的对象
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
// 创建索引的请求
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("ysx_course");
// 指定 ES 库分片的数量和副本的数量
request.settings(Settings.builder().put("number_of_shards", "1").put("number_of_replicas", "0"));
// 创建映射
// 在创建索引的时候可以将映射一起指定了
// "doc" 是 type (相当于 table name)
request.mapping("doc", "{\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"description\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"search_analyzer\": \"ik_smart\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"search_analyzer\": \"ik_smart\"\n" +
" },\n" +
"\"pic\":{ \n" +
"\"type\":\"text\", \n" +
"\"index\":false \n" +
"}, \n" +
" \"price\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"float\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"studymodel\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"timestamp\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"date\",\n" +
" \"format\": \"yyyy-MM‐dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy‐MM‐dd||epoch_millis\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }", XContentType.JSON);
// 执行创建操作
CreateIndexResponse response = indices.create(request);
// 得到响应
boolean b = response.isAcknowledged()
{
"properties": {
"description": { // 课程描述
"type": "text", // String text 类型
"analyzer": "ik_max_word", // 存入的分词模式:细粒度
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart" // 查询的分词模式:粗粒度
},
"name": { // 课程名称
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"pic":{ // 图片地址
"type":"text",
"index":false // 地址不用来搜索,因此不为它构建索引
},
"price": { // 价格
"type": "scaled_float", // 有比例浮点
"scaling_factor": 100 // 比例因子 100
},
"studymodel": {
"type": "keyword" // 不分词,全关键字匹配
},
"timestamp": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
// 查询
// 搜索请求对象
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("ysx_course"); // 指定 index name
// 指定类型
searchRequest.types("doc");
// 搜索源构建对象
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
// 搜索方式
//
// matchAllQuery搜索全部
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
//
// 精确查询 TermQuery
// 在搜索时会整体匹配关键字,不再将请求中的关键字分词
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("studymodel", "201002"));
// 根据 id 查
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("_id", "1"));
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termsQuery("_id", "1"));
//
// MatchQuery 即全文检索,会对关键字进行分词后匹配词条。
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("description", "Spring开发框架")
// 匹配占比
// 设置"minimum_should_match": "80%"表示,三个词在文档的匹配占比为80%,即3*0.8=2.4,向下取整得2,表示至少有两个词在文档中要匹配成功。
.minimumShouldMatch("70%"));
//
// 多字段联合搜索 MultiQuery
// 假如用户输入了某关键字,我们在查找的时候并不知道他输入的是 name 还是 description,这时我们用什么都不合适,而 MultiQuery 的出现解决了这个问题
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery("Spring开发框架", "name", "description").minimumShouldMatch("70%"))
.field("name", 10)); // 设置 name 10倍权重, 比重越高的域当他符合条件时计算的得分越高,相应的该记录也更靠前。
//
// 布尔查询 BoolQuery
// 如果我们既要对一些字段进行分词查询,同时要对另一些字段进行精确查询,就需要使用布尔查询来实现了
// 有三个可选的参数:
// must:文档必须匹配must所包括的查询条件,相当于 “AND”
// should:文档应该匹配should所包括的查询条件其中的一个或多个,相当于 "OR"
// must_not:文档不能匹配must_not所包括的该查询条件,相当于“NOT”
//
// 首先构造多关键字查询条件
MultiMatchQueryBuilder matchQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery("Spring开发框架", "name", "description").field("name", 10);
// 然后构造精确匹配查询条件
TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.termQuery("studymodel", "201002");
// 组合两个条件,组合方式为 must 全满足
BoolQueryBuilder boolQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
boolQueryBuilder.must(matchQueryBuilder);
boolQueryBuilder.must(termQueryBuilder);
// 定义过滤器查询,是在原本查询结果的基础上对数据进行筛选
// 推荐尽量使用过虑器去实现查询
// 过滤器在布尔查询中使用
// 注意:range和term一次只能对一个Field设置范围过虑。
boolQueryBuilder.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("studymodel", "201001"));
boolQueryBuilder.filter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").gte(60).lte(100));
// 将查询条件封装给查询对象
searchSourceBuilder.query(boolQueryBuilder);
// 设置源字段过虑,第一个参数结果集包括哪些字段,第二个参数表示结果集不包括哪些字段
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"name","studymodel","price","timestamp"},new String[]{});
// 分页
int page = 2; // 页码
int size = 1; // 每页显示的条数
int index = (page - 1) * size;
searchSourceBuilder.from(index);
searchSourceBuilder.size(1);
// 排序
// 我们可以在查询的结果上进行二次排序,支持对 keyword、date、float 等类型添加排序,text类型的字段不允许排序
searchSourceBuilder.sort("studymodel", SortOrder.DESC); // 第一排序规则
searchSourceBuilder.sort("price", SortOrder.ASC); // 第二排序规则
// 高亮查询
HighlightBuilder highlightBuilder = new HighlightBuilder();
highlightBuilder.preTags("<em>"); // 高亮前缀
highlightBuilder.postTags("</em>"); // 高亮后缀
highlightBuilder.fields().add(new HighlightBuilder.Field("name")); // 高亮字段
// 添加高亮查询条件到搜索源
searchSourceBuilder.highlighter(highlightBuilder);
// 向搜索请求对象中设置搜索源
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = client.search(searchRequest);
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
// 匹配到的总记录数
long totalHits = hits.getTotalHits();
// 得到匹配度高的文档
SearchHit[] searchHits = hits.getHits();
for(SearchHit hit:searchHits){
// 文档的主键
String id = hit.getId();
// 源文档内容
Map<String, Object> sourceAsMap = hit.getSourceAsMap();
String name = (String) sourceAsMap.get("name");
// 由于前边设置了源文档字段过虑,这时description是取不到的
String description = (String) sourceAsMap.get("description");
String studymodel = (String) sourceAsMap.get("studymodel");
Double price = (Double) sourceAsMap.get("price");
Date timestamp = dateFormat.parse((String) sourceAsMap.get("timestamp"));
// 高亮文本
Map<String, HighlightField> highlightFields = hit.getHighlightFields();
}
集成 influxdb
influx
show databases
create database "test"
select * from ApiQPS order by time desc;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.influxdb</groupId>
<artifactId>influxdb-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
or
<!-- 针对 2.x 版本的client lib -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.influxdb</groupId>
<artifactId>influxdb-client-java</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
</dependency>
这里以 1.x 为例
@Service
@AllArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class Monitor {
private InfluxDB influxDB;
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000)
public void writeQPS() {
// 模拟要上报的统计数据
int count = (int) (Math.random() * 100);
Point point = Point.measurement("ApiQPS") // ApiQPS表
.tag("url", "/hello") // url字段
.addField("count", count) // 统计数据
.time(System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) // 时间
.build();
// 往test库写数据
influxDB.write("test", "autogen", point);
log.info("上报统计数据:" + count);
}
15.1. canal 订阅
https://github.com/zendesk/maxwell 类似
https://github.com/alibaba/otter
15.2. mybatis 自动建表插件
https://github.com/zyf970617/mybatis-auto-create-table
https://blog.csdn.net/yuru974882032/article/details/106749299
https://gitee.com/sunchenbin/mybatis-enhance
https://gitee.com/baomidou/mybatis-mate-examples?_from=gitee_search
15.3. mybatis crud 增强插件
mybatis plus
tk.mybatis
15.4. 数据库迁移版本控制
两者差别不大,因功能多,个人“稍微”倾向 Liquibase; 一般我的倾向是小项目,整体变动不大的用Flyway,而大应用和企业应用用Liquibase更合适
https://github.com/bytebase/bytebase 新的更为全面的数据库 schema 管理工具
15.4.1. liquibase
15.4.2. Flyway
15.4.2.1. working process 工作原理
项目启动,应用程序完成数据库连接池的建立后,Flyway自动运行。
初次使用时,flyway会创建一个 flyway_schema_history 表,用于记录sql执行记录。
Flyway会扫描项目指定路径下(默认是 classpath:db/migration )的所有sql脚本,检查已经执行过的版本对应的脚本是否发生变化,包括脚本文件名,以及脚本内容, 与项目中的sql脚本若不一致,Flyway会报错并停止项目执行。
如果校验通过,则根据表中的sql成功记录最大版本号,忽略所有版本号小于该版本的脚本。再按照版本号从小到大,逐个执行其余脚本。
15.4.2.2. how to verify the sql update 校验原理
如何校验文件?
Flyway获取 flyway_schema_history 中最新成功记录的版本号(基准version),与项目中db/migration目录中的脚本version进行比对,当脚本version大于基准version则执行。
对于修改已经执行过的sql脚本,Flyway也有预防,那就是checksum。每个sql脚本在执行前会将基本信息写入flyway_schema_history中,Flyway会把每个脚本作为输入,通过一系列算法输出一个整数值checksum来判断脚本是否有修改(哪怕是一个空格),Flyway在工作之前,会逐个脚本比对其数据库中的checksum值,如果计算结果不同,则会报mismatch的错误
15.4.2.3. how to use flyway
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flywaydb</groupId>
<artifactId>flyway-core</artifactId>
<version>7.1.1</version>
</dependency>
spring:
# 数据库连接配置
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/flyway_demo?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: root
flyway:
# 是否启用flyway, 默认就是开启的
enabled: true
# 编码格式,默认UTF-8
encoding: UTF-8
# 迁移sql脚本文件存放路径,默认db/migration
locations: classpath:db/migration
check-location: true #检查迁移脚本的位置是否存在,默认false.
table: schema_version_synchronizer #配置数据库信息表的名称,默认是 flyway_schema_history。
# 迁移sql脚本文件名称的前缀,默认V
#
sql-migration-prefix: V
# 迁移sql脚本文件名称的分隔符,默认2个下划线__
sql-migration-separator: __
# 迁移sql脚本文件名称的后缀
sql-migration-suffixes: .sql
# 迁移时是否进行校验,默认true
validate-on-migrate: true
# 升级一个空的数据库,或者在一直使用flyway升级方案的数据库上进行升级,都不会又问题。但是,如果在已有的数据库引入flyway,就需要一些额外的工作。
# 设置此属性 true, 表示当迁移发现数据库非空且存在没有元数据的表时,自动执行基准迁移,新建schema_version表
# flyway会自动将当前的数据库记录为V1版本,然后执行升级脚本。这也表示用户所准备的脚本中,V1版本的脚本会被跳过,只有V1之后的版本才会被执行
# 默认 false
baseline-on-migrate: true
# 是否允许无序的迁移,默认false
out-of-order: true
clean-disabled: true #flyway 的 clean 命令会删除指定 schema 下的所有 table, 生产务必禁掉。这个默认值是 false 理论上作为默认配置是不科学的。
命名规则:
仅需要被执行一次的SQL命名以大写的"V"开头,V + 版本号(版本号的数字间以”.“或”_“分隔开) + 双下划线(用来分隔版本号和描述) + 文件描述 + 后缀名。例如: V20201100__create_user.sql、V2.1.5__create_user_ddl.sql、V4.1_2__add_user_dml.sql 。
可重复运行的SQL,则以大写的“R”开头,后面再以两个下划线分割,其后跟文件名称,最后.sql结尾,比如: R__truncate_user_dml.sql ,但一般不推荐使用。(只要脚本内容发生了变化,启动时候就会执行)
更详细配置
flyway.baseline-description对执行迁移时基准版本的描述.
flyway.baseline-on-migrate当迁移时发现目标schema非空,而且带有没有元数据的表时,是否自动执行基准迁移,默认false.
flyway.baseline-version开始执行基准迁移时对现有的schema的版本打标签,默认值为1.
flyway.check-location检查迁移脚本的位置是否存在,默认false.
flyway.clean-on-validation-error当发现校验错误时是否自动调用clean,默认false.
flyway.enabled是否开启flywary,默认true.
flyway.encoding设置迁移时的编码,默认UTF-8.
flyway.ignore-failed-future-migration当读取元数据表时是否忽略错误的迁移,默认false.
flyway.init-sqls当初始化好连接时要执行的SQL.
flyway.locations迁移脚本的位置,默认db/migration.
flyway.out-of-order是否允许无序的迁移,默认false.
flyway.password目标数据库的密码.
flyway.placeholder-prefix设置每个placeholder的前缀,默认${.
flyway.placeholder-replacementplaceholders是否要被替换,默认true.
flyway.placeholder-suffix设置每个placeholder的后缀,默认}.
flyway.placeholders.[placeholder name]设置placeholder的value
flyway.schemas设定需要flywary迁移的schema,大小写敏感,默认为连接默认的schema.
flyway.sql-migration-prefix迁移文件的前缀,默认为V.
flyway.sql-migration-separator迁移脚本的文件名分隔符,默认__
flyway.sql-migration-suffix迁移脚本的后缀,默认为.sql
flyway.tableflyway使用的元数据表名,默认为schema_version
flyway.target迁移时使用的目标版本,默认为latest version
flyway.url迁移时使用的JDBC URL,如果没有指定的话,将使用配置的主数据源
flyway.user迁移数据库的用户名
flyway.validate-on-migrate迁移时是否校验,默认为true.
和 Maven 插件配合使用: (maven插件让我们可以不需要启动项目就能执行Flyway的各种命令)
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.flywaydb</groupId>
<artifactId>flyway-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>5.2.4</version>
<configuration>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/flyway_demo?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
</url>
<user>root</user>
<password>root</password>
<driver>com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</driver>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
1.baseline
对已经存在数据库Schema结构的数据库一种解决方案。
实现在非空数据库新建MetaData表,并把Migrations应用到该数据库;也可以在已有表结构的数据库中实现添加Metadata表。
2.clean(非常危险)
清除掉对应数据库Schema中所有的对象,包括表结构,视图,存储过程等,clean操作在dev 和 test阶段很好用,但在生产环境务必禁用。
3.info
用于打印所有的Migrations的详细和状态信息,也是通过MetaData和Migrations完成的,可以快速定位当前的数据库版本。
4.migrate
执行迁移,等同于项目启动执行的内容
5.repair
修复metaData表,该操作在metadata出现错误时很有用。
6.undo(社区版本不支持)
撤销操作
7.validate
验证已经执行的Migrations是否有变更,默认开启的,原理是对比MetaData表与本地Migrations的checkNum值,如果值相同则验证通过,否则失败。
15.5. 数据库连接字符串收集
MySQL
jdbc:mysql://122.191.199.51:60000/js_phaseii_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=true
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
oracle:
1.使用service_name,配置方式: jdbc:oracle:thin:@//:1521/helowin
jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE
jdbc:oracle:thin:@//10.20.32.19:1521/ORCLPDB1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
2.使用SID,配置方式(@后没'//'): jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521/helowin
3.使用oci,配置方式: jdbc:oracle:oci:@localhost:1521:XE
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
postgres:
语法: jdbc:postgresql://[user[:password]@][netloc][:port][/dbname][?param1=value1&...]
jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/test
postgresql://other@localhost/otherdb?connect_timeout=10&application_name=myapp
postgresql://localhost/mydb?user=other&password=secret
driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
15.6. graphql集成
https://www.awaimai.com/2876.html
https://juejin.cn/post/6982083422567006245 入门 https://graphql.cn/learn/queries/ 官网文档
15.7. 启动执行 SQL
15.7.1. 利用 spring jdbc
spring:
datasource:
# 数据源基本配置
username: root
password: 123
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=UTC
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# 数据源其他配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
# 配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,'wall'用于防火墙
filters: stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
schema:
- classpath:sql/department.sql
- classpath:sql/employee.sql
data: classpath:data.sql
sql-script-encodng: utf-8
initialization-mode: ALWAYS
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: none
15.7.2. 使用 jpa
1、SpringBoot根据脚本初始化
结构初始化脚本文件由spring.datasource.schema属性指定,数据初始化脚本由文件spring.datasource.data属性指定。
这两个脚本是否执行的开关由spring.datasource.initialization-mode决定:always-一定执行,embedded-只对内存数据库执行(默认),never-不执行。
spring.jpa.defer-datasource-initialization setup to true will enable the insertting sql execution, no other configuraton setup. Just need a new sql file named with "data.sql" in resources folder.
2、JPA根据类结构初始化
@Entity注解的类将会被初始化一张数据库表。
是否执行的开关由spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto属性控制,可为create/update/create-drop/none/validate,其中none和validate为不执行。
3、初始化时对于另一个属性spring.jpa.generate-dll在理解上的困惑
按照它的描述,spring.jpa.generate-dll是jpa层面对数据表生成策略的控制,而spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto是jpa实现hibernate层面上对数据表生成策略的控制。
实践也验证了文章里所说的,spring.jpa.generate-dll比spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto有更强的控制力度,即使spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto为none,只要spring.jpa.generate-dll为true,也会根据@Entity注解的实体类生成对应数据表。
按照文章的建议,为了避免混淆和不好理解,这两者最好不要混用,只对JPA实现层面的控制属性spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto进行设置即可。
最保险的做法: 若想自动生成表, setup spring.jpa.generate-dll=true, spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto 则设置为需要的策略; 若不想自动生成表, 设置 generate-ddl=false (默认) 即可
4、让SpringBoot根据脚本和让JPA根据实体类进行初始化,两者之中选择一个即可。
5 spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect 虽然 不同的数据库方言会自动选择, 但是若想使用特定引擎类型需要指定方言, 不加这句则不会默认创建MyISAM引擎的数据库
spring:
jpa:
database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
generate-ddl: true
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create/create-drop/update/validate/none
1.·create:每次加载hibernate时都会删除上一次的生成的表,然后根据你的model类再重新来生成新表,
2.·create-drop:每次加载hibernate时根据model类生成表,但是sessionFactory一关闭,表就自动删除。
create/create-drop 在创建表时, 默认会扫描 classpath 下面(项目中一般是 resources 目录)是否有import.sql,如果有机会执行import.sql脚本中的 insert 语句
3.·update:最常用的属性,第一次加载hibernate时根据model类会自动建立起表的结构(前提是先建立好数据库),以后加载hibernate时根据model类自动更新表结构,即使表结构改变了但表中的行仍然存在不会删除以前的行。要注意的是当部署到服务器后,表结构是不会被马上建立起来的,是要等应用第一次运行起来后才会。
4.·validate:每次加载hibernate时,验证创建数据库表结构,只会和数据库中的表进行比较,不会创建新表,但是会插入新值。
推荐在初次创建时会设为create,创建好后改为validate. (进开发环境使用, 生产环境慎用)
15.7.3. DataSourceInitializer
@Configuration
public class CustomizeDataSourceInitializer {
@Value("classpath:testSql/test_farms.sql")
private Resource functionScriptFarms;
@Value("classpath:testSql/test_miners.sql")
private Resource functionScriptMiners;
@Value("classpath:testSql/test_pool_config.sql")
private Resource functionScriptPoolConfig;
@Bean
public DataSourceInitializer dataSourceInitializer(final DataSource dataSource) {
final DataSourceInitializer initializer = new DataSourceInitializer();
// 设置数据源
initializer.setDataSource(dataSource);
initializer.setDatabasePopulator(databasePopulator());
return initializer;
}
private DatabasePopulator databasePopulator() {
final ResourceDatabasePopulator populator = new ResourceDatabasePopulator();
populator.addScripts(functionScriptFarms);
populator.addScripts(functionScriptMiners);
populator.addScripts(functionScriptPoolConfig);
return populator;
}
}
15.7.4. maven-antrun-pluginn
<profile>
<id>refresh-db</id>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-antrun-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<target>
<property file="src/main/resources/application.properties" />
<sql driver="${jdbc.driver}" url="${jdbc.url}" userid="${jdbc.username}" password="${jdbc.password}" onerror="continue" encoding="${project.build.sourceEncoding}">
<classpath refid="maven.test.classpath" />
<transaction src="src/main/resources/sql/h2/schema.sql"/>
<transaction src="src/test/resources/data/h2/import-data.sql"/>
</sql>
</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</profile>
15.7.5. construct a script execution service manually
https://mubasil-bokhari.medium.com/execute-sql-script-in-spring-boot-30636884a932 todo
15.8. 整合 spring jdbc
定义映射类:
- @Table:映射自定义的表名。非JPA注解
- @Column:映射自定义的列名,非JPA注解
- @Id:修饰标识属性,非JPA注解
- @PersistenceConstructor:修饰主构造器。当你的映射类中有多个构造器时,
你希望Spring Data JDBC用哪个构造器来创建对象,
就用该注解来修饰该构造器。
在DAO接口中让DAO接口继承CrudRepository或PagingAndSortingRepository。
定义方法名关键字查询、
findByNameLike(xxx)
findByAgeGreaterThan
findByAgeLessThan
findByAgeBetween
@Query查询、
@query("select * from user_info where password like :pwd")
List<User> findBySql(String pwd);
@query("update xxx set name = :name where age between :startAge and :endAge")
@Modifying
int updateNamebyAge(int startAge, int endAge, String name);
完全自定义查询
即可用DataSource,也用JdbcTemplate。
//创建数据库连接
Connection connection = this.dataSource.getConnection();
//创建 PreparedStatement 预处理语句
PreparedStatement pstmt = connection.prepareStatement("select * from user_inf where name like ?");
pstmt.setString(1, namePattern);
//执行查询
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历结果集,封装对象
while (rs.next())
{
userList.add(new User(
rs.getInt("user_id"),
rs.getString("name"),
rs.getString("password"),
rs.getInt("age")
));
}
//直接执行查询
List<User> userList = this.jdbcTemplate.query(
"select user_id as id,name ,password,age from user_inf where name like ?",
//把查询的结果封装起来
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class),
namePattern
);
15.9. 整合 hibernate (即 jpa)
https://github.com/raeperd/realworld-springboot-java
15.9.1. jpa注解总结
// anno on class
@DynamicInsert
@DynamicUpdate
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
//anno on field
// uuid as primary key
@Id
@GenericGenerator(name = "generator", strategy = "uuid")
@GeneratedValue(generator = "generator", strategy = GenerationType.TABLE)
@Column(name = "id", length = 32)
15.9.2. 使用枚举
15.9.2.1. the basic usage
public enum Rating {
UNRATED,
G,
PG,
PG13,
R,
NC17
}
@Entity
public class Movie {
/**
* to persist string (the field name) into db,
* (and there is a another value here: ordinal, which is default, that means persist int (the ordr number) to db)
*/
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
private Rating rating;
}
15.9.2.2. @Converter (推荐)
public enum Category {
SPORT("S"), MUSIC("M"), TECHNOLOGY("T");
@Entity
public class Article {
@column(...)
private Category category;
// We've set the @Converter‘s value of autoApply to true so that JPA will automatically apply the conversion logic to all mapped attributes of a Category type. Otherwise, we'd have to put the @Converter annotation directly on the entity's field.
@Converter(autoApply = true)
public class CategoryConverter implements AttributeConverter<Category, String> {
@Override
public String convertToDatabaseColumn(Category category) {
if (category == null) {
return null;
}
return category.getCode();
}
@Override
public Category convertToEntityAttribute(String code) {
if (code == null) {
return null;
}
return Stream.of(Category.values())
.filter(c -> c.getCode().equals(code))
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(IllegalArgumentException::new);
}
}
15.9.2.3. @PostLoad and @PrePersist
@Entity
public class Article {
// mapping to db
@Basic
private int priorityValue;
// store the enum value
@Transient
private Priority priority;
@PostLoad
void fillTransient() {
if (priorityValue > 0) {
this.priority = Priority.of(priorityValue);
}
}
@PrePersist
void fillPersistent() {
if (priority != null) {
this.priorityValue = priority.getPriority();
}
}
15.9.3. jpa queryDsl 多表联查
https://github.com/querydsl/querydsl
https://zhongpan.tech/2020/07/20/034-best-practice-of-multi-table-joint-query-in-spring-data-jpa/ https://www.baeldung.com/querydsl-with-jpa-tutorial
15.9.4. jpa 支持 java8 time
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54840769/how-to-persist-localdate-with-jpa
https://www.baeldung.com/jpa-java-time
15.9.5. 审计 createdDate
https://blog.csdn.net/a972669015/article/details/104778172 TODO
15.9.6. 执行原生 SQL
/*
- 只需要在后面加一个 nativeQuery = true 就行
- 参数用
*/
@Query(value = "select xx from where a = :userId", nativeQuery = true)
List<Long> findFriendsByUserId(@param("userId)Long userId);
or
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
@Override
public List<Employee> getFirstNamesLikeAndBonusBigger(String firstName, Double bonusAmount) {
Query query = entityManager.createNativeQuery("select e.* from spring_data_jpa_example.bonus b, spring_data_jpa_example.employee e\n" +
"where e.id = b.employee_id " +
"and e.firstname LIKE ? " +
"and b.amount> ? ", Employee.class);
query.setParameter(1, firstName + "%");
query.setParameter(2, bonusAmount);
return query.getResultList();
}
or
public class CustomPostRepositoryImpl implements CustomPostRepository {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Override
public List<PostDTO> findPostDTOByTitle(
@Param("postTitle") String postTitle) {
return entityManager.createNativeQuery("""
SELECT p.id AS p_id,
p.title AS p_title,
pc.id AS pc_id,
pc.review AS pc_review
FROM post p
JOIN post_comment pc ON p.id = pc.post_id
WHERE p.title LIKE :postTitle
ORDER BY pc.id
""")
.setParameter("postTitle", postTitle)
.unwrap(org.hibernate.query.Query.class)
.setResultTransformer(new PostDTOResultTransformer())
.getResultList();
}
}
15.9.7. 动态 SQL
https://www.cnblogs.com/kongxianghai/p/7575988.html
插入和修改可以在类实体上标注 @DynamicInsert和@DynamicUpdate 运行时动态生成非空字段的 插入和 更新语句
动态查询则需要用 Criteria API
15.9.8. spring-data-rest 配合 spring-data-jpa
http://docs.jcohy.com/docs/spring-data-rest/3.2.8.RELEASE/html5/zh-cn/ https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/rest/docs/3.4.5/reference/html/#Project
https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/docs/2.4.5/reference/html/#repositories
spring data rest 可以直接将 repository 发布为 rest service, 和 spring data jpa (自动生成 crud api) 配合
目前支持Spring Data JPA、Spring Data MongoDB、Spring Data Neo4j、Spring Data GemFire、Spring Data Cassandra的 repository 自动转换成REST服务
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
@RepositoryRestResource // publish repository as rest service
interface ReservationRepository extends JpaRepository<Reservation, Long> {
/**
* customized rest service
*
* http://localhost:8080/reservations/search/by-name?name=hello
*/
@RestResource(path = "by-name")
Optional<Reservation> findByName(String name);
}
在分布式下, 在 feign client 接收 spring data rest 发布的 service 需要和 hateoas (spring-boot-starter-hateoas) 配合:(hateoas 版本更新, 接受数据的实体有改变)
@FeignClient("reservation-service") // also support 'url' ( outside eureka)
interface ReservationResources {
@RequestMapping("/reservations")
CollectionModel<Reservation> reservations();
@RequestMapping("/message")
String message();
}
15.10. 整合 mybatis-plus
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
public interface IAccountService extends IService<Account> {
}
@Service
public class AccountService extends ServiceImpl<AccountMapper, Account> implements IAccountService {
}
@mapper
// 或者启动类 @MapperScan("io.github.xiaoyureed.workflow.mapper")
public interface AccountMapper extends BaseMapper<Account> {
}
AccountMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org/DTD Mapper 3.0" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="io.github.xiaoyureed.workflow.mapper.AccountMapper">
</mapper>
15.11. 整合 mybatis
https://github.com/gothinkster/spring-boot-realworld-example-app
- 依赖:mybatis-spring-boot-starter
- @Mapper标注创建的xxxMapper接口;或者 在 启动类上 标注 @mapperscan(basepackage...)
- @Select("SELECT * FROM USER WHERE NAME = #{name}")标注方法,还有@insert等;方法参数@Param("name")标注
- 通过@Autowired注入使用
也可以直接引入 mybatisplus-spring-boot-starter 通过 mybatis plus 使用
15.11.1. 基本配置
server:
port: 8080
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mall?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: root
mybatis:
# config-location属性和configuration属性不能同时指定
#config-location: classpath:mybatis.xml
type-aliases-package: me.zingon.pagehelper.model
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
#mapper-locations: {"classpath:mapper/*.xml", "classpath*:com/**/mapper/*.xml"}
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
default-fetch-size: 100
default-statement-timeout: 30
15.11.2. 使用 拦截器 interceptor plugins
15.11.2.1. principle of plugins
基于插件机制,基本上可以控制SQL执行的各个阶段,如执行阶段,参数处理阶段,语法构建阶段,结果集处理阶段,具体可以根据项目业务来实现对应业务逻辑。
设计模式:代理模式、责任链模式
15.11.2.2. use scenarios
- paging 拦截StatementHandler类的prepare方法,改变要执行的SQL语句为分页语句即可;
- Assign default values to fields before SQL execution
- SQL performance monitor 通过拦截Executor类的update, query等方法,用日志记录每个方法执行的时间
15.11.2.3. how to use plugins
实现 Interceptor 接口, 标注@Intercepts(@Signature) , 参考 https://www.jianshu.com/p/0a72bb1f6a21
scenario 1: 直接给自定义拦截器添加一个 @Component注解 , 启动时不会自动调用自定义拦截器的setProperties方法 scenario 2: 无需 @component ,只需要 @bean ConfigurationCustomizer 中 addInterceptor , 不会自动调用setProperties方法 --- mybatis plus 中的配置方法 scenario 3: 无需 @component ,需要 @bean SqlSessionFactoryBean 中 setPlugins --- (app 启动时, setProperties被自动调用)
/**
* 在mybatis中可被拦截的类型有四种(按照拦截顺序):
* <p>
* Executor:执行 SQL 语句。
* ParameterHandler:处理参数
* ResultHandler:处理结果集。
* StatementHandler:Sql语法构建。
*
* 每个类型可以被拦截的方法:
*
拦截的类 拦截的方法
Executor update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback,getTransaction, close, isClosed
ParameterHandler getParameterObject, setParameters
StatementHandler prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query
ResultSetHandler handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters
*/
//标识该类是一个拦截器;
@Intercepts({
//指明自定义拦截器需要拦截哪一个类型,哪一个方法(方法有重载, 所以还需要 指明 args 才能确定是哪个方法)
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "update", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {
MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
private static class SqlInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Object target = invocation.getTarget(); //被代理对象
// Method method = invocation.getMethod(); //代理方法
// Object[] args = invocation.getArgs(); //方法参数
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
Object param = null;
MappedStatement mappedStatement = (MappedStatement) args[0];
if (args.length > 1) {
param = args[1];
}
String sql = sql(mappedStatement, param);
return invocation.proceed();
}
private String sql(MappedStatement statement, Object param) {
BoundSql boundSql = statement.getBoundSql(param);
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
//将原始sql中的空白字符(\s包括换行符,制表符,空格符)替换为" "
String sql = boundSql.getSql().replaceAll("[\\s]+", " ");
if (param == null || parameterMappings.size() == 0) {
return sql;
}
org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration configuration = statement.getConfiguration();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(param.getClass())) {
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", getParameterValue(param));
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(param);
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (metaObject.hasGetter(propertyName)) {
Object obj = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", getParameterValue(obj));
} else if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
Object obj = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", getParameterValue(obj));
}
}
}
return sql;
}
private String getParameterValue(Object obj) {
String value = null;
if (obj instanceof String) {
value = "'" + obj.toString() + "'";
} else if (obj instanceof Date) {
DateFormat formatter = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.DEFAULT, DateFormat.DEFAULT, Locale.CHINA);
value = "'" + formatter.format(obj) + "'";
} else {
if (obj != null) {
value = obj.toString();
} else {
value = "";
}
}
return value;
}
/**
* 生成代理对象
* 可选
* 我们可以决定是否要进行拦截, 如果拦截, 就返回代理后的对象
* * 如果不拦截, 则返回原始对象
*
* 每经过一个拦截器对象都会调用插件的plugin方法,也就是说,该方法会调用4次。根据@Intercepts注解来决定是否进行拦截处理
*/
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
//返回四大接口对象的代理对象, 表示始终会执行拦截
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
// 控制是否拦截
// 若类上加了 @Signature 指明了 拦截类型, 这一步就省了
// if (target instanceof StatementHandler) {
// return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
// }
// return target;
}
/**
* 可选
* 用于在 Mybatis 配置文件中指定一些属性的。类似 spring 中有 @value,
* 一般不用
*/
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
}
15.11.3. typehandler
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37735176/article/details/103107759 https://www.cnblogs.com/haoliyou/p/13743698.html https://www.cnblogs.com/dyf-stu/p/10162301.html
15.11.4. 全注解开发
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/94554180 TODO
15.11.5. 动态定时刷新 SQL mapper 实现热加载
https://veevv.com/2015/09/30/mybatis-mapper-xml-reloader/
@component
public class XMLMapperReloader implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
private HashMap<String, Long> fileMapping = new HashMap<String, Long>();
private Scanner scanner = null;
private String packageSearchPath = "classpath:com/xx/xx/dao/*/*.xml";
private ScheduledExecutorService service = null;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.context = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext;
}
public XMLMapperReloader(){
service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
service.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Task(), 5, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
class Task implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
scanner = new Scanner();
scanner.refreshMapper();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes" })
class Scanner {
private Resource[] mapperLocations;
public void refreshMapper() {
try {
SqlSessionFactory factory = context.getBean(SqlSessionFactory.class);
Configuration configuration = factory.getConfiguration();
// step.1 扫描文件
try {
this.scanMapperXml();
} catch (IOException e) {
return;
}
// step.2 判断是否有文件发生了变化
if (this.isChanged()) {
System.out.println("==============检测到mapper有改变, 开始刷新...===============");
// step.2.1 清理
this.removeConfig(configuration);
// step.2.2 重新加载
for (Resource configLocation : mapperLocations) {
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(configLocation.getInputStream(), configuration, configLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (IOException e) {
continue;
}
}
System.out.println("==============mapper刷新完毕===============");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void scanMapperXml() throws IOException {
this.mapperLocations = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
}
private void removeConfig(Configuration configuration) throws Exception {
Class<?> classConfig = configuration.getClass();
clearMap(classConfig, configuration, "mappedStatements");
clearMap(classConfig, configuration, "caches");
clearMap(classConfig, configuration, "resultMaps");
clearMap(classConfig, configuration, "parameterMaps");
clearMap(classConfig, configuration, "keyGenerators");
clearMap(classConfig, configuration, "sqlFragments");
clearSet(classConfig, configuration, "loadedResources");
}
private void clearMap(Class<?> classConfig, Configuration configuration, String fieldName) throws Exception {
Field field = classConfig.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
Map mapConfig = (Map) field.get(configuration);
mapConfig.clear();
}
private void clearSet(Class<?> classConfig, Configuration configuration, String fieldName) throws Exception {
Field field = classConfig.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
Set setConfig = (Set) field.get(configuration);
setConfig.clear();
}
private boolean isChanged() throws IOException {
boolean flag = false;
for (Resource resource : mapperLocations) {
String resourceName = resource.getFilename();
boolean addFlag = !fileMapping.containsKey(resourceName);// 此为新增标识
// 修改文件:判断文件内容是否有变化
Long compareFrame = fileMapping.get(resourceName);
long lastFrame = resource.contentLength() + resource.lastModified();
boolean modifyFlag = null != compareFrame && compareFrame.longValue() != lastFrame;// 此为修改标识
// 新增或是修改时,存储文件
if(addFlag || modifyFlag) {
fileMapping.put(resourceName, Long.valueOf(lastFrame));// 文件内容帧值
flag = true;
}
}
return flag;
}
}
public String getPackageSearchPath() {
return packageSearchPath;
}
public void setPackageSearchPath(String packageSearchPath) {
this.packageSearchPath = packageSearchPath;
}
}
15.11.6. 自定义资源文件打包目录 and 开启占位符过滤
mapper.xml 和 dao interface 放在一起: (开启资源文件过滤)
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<!-- maven 默认仅仅 将src/main/resources 下的文件打包到 jar
若 mapper.xml 不在标准目录下, 需要指定资源过滤处理 -->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
<!-- 打包到哪里? 可省略, 默认 jar 根目录 -->
<!-- <targetPath>META-INF/plexus</targetPath> -->
<!-- 是否开启资源文件占位符过滤 (如 ${project.version}), 默认 false -->
<!-- <filtering>false</filtering> -->
</resource>
<!-- 可省略 -->
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<!-- 添加额外的配置文件, 用来解析资源文件中的占位符 -->
<filters>
<filter>src/main/filters/filter.properties</filter>
</filters>
</resources>
</build>
15.12. 事务
15.12.1. 事务基本使用
15.12.1.1. 手动编程实现
// spring provide TransactionManager interface
// 各个厂商去实现然后注入到Spring容器中就就好了, for example : Spring-jdbc -> org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
TransactionStatus transaction =
//DefaultTransactionDefinition 定义隔离界别, 传播方式
transactionManager.getTransaction(new DefaultTransactionDefinition());
try {
jdbcTemplate.update("UPDATE info_user SET sex = ? WHERE user_name = ?","女","lisi");
System.out.println("一段薛定谔的逻辑");
transactionManager.commit(transaction);
} catch (DataAccessException e) {
transactionManager.rollback(transaction);
}
// or
//
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
public void save(ArtisanDto artisanDto) {
transactionTemplate.execute(transactionStatus -> {
artisanDao.save(artisanDto);
//....
// .....
return Boolean.TRUE;
});
}
15.12.1.2. 注解声明式
只需要在类或者方法上添加@Transactional注解即可
@EnableTransactionManagement 默认就开启了, 可加可不加
- proxyTargetClass 控制是否一定使用 cglib 生成代理类
默认 false, 此时事务类实现了接口的使用JDK代理,未实现接口的使用CGLIB代理, 当proxyTargetClass = true时,无论target是否实现了接口,其都是CGLIB代理
- mode 控制Advice切面如何被应用(如何被织入)
默认 PROXY 模式, 通过代理调用拦截实现通知增强,本地调用(即通过 this.xxx())不能实现通知增强;
AdviceMode.ASPECTJ模式, 这种情况下proxyTargetClass属性将会被忽略,其将通过编译时字节码增强的方式织入切面, 这种情况下不涉及代理,本地调用也同样生效。需要注意,这种情况下需要引入 spring-aspects 模块 jar包
如果事务类没有实现接口, 推荐基于AspectJ编译期织入来实现, @EnableTransactionManagement(mode = AdviceMode.ASPECTJ)
// 最严格, 效率最低
// 这个隔离级别可以防止出现脏读,不可重复读和幻读,并且设置回归的异常类型为Exception,这个很重要哦,因为rollbackFor的默认值为RuntimeException运行时异常
@tranfactional(isolation=serializable, rollbackfor=exception.class)
// 如果想自己捕获异常, 不抛出异常, 然后回滚, 可以在 catch 里面拿到当前的事务设置回滚:
TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly()
15.12.1.3. 事务同步
// 事务同步
// https://www.jdon.com/57371.html
// 如何保证逻辑 A 所在的事务成功后才做某些操作B
// 把A用try-catch包裹, 然后在finally里面获取当前事务的状态然后再决定是否执行 B --> 可以, 但不优雅
// 可以利用TransactionSynchronization
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.SERIALIZABLE, rollbackFor = Exception.class)
void a() {
// 操作 A
// ...
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new TransactionSynchronization() {
@Override
public void afterCommit() {
//操作 B
//...
}
});
}
// 如何在事务失败回滚后, 执行逻辑 C?
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.SERIALIZABLE, rollbackFor = Exception.class)
void a() {
// 操作 A
// ...
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new TransactionSynchronization() {
@Override
public void afterCompletion(int status) {
if (status == TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK) {
// 逻辑 C
}
if (status == TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED) {
// 逻辑 B
}
}
});
}
15.12.2. transaction not working
事务不生效, 可能是:
- 可能是数据库引擎不支持事务
mysql默认引擎INNODB是支持的,但MYISAM是不支持的;
- 如果是非 spring boot 项目, 没有启动自动配置, 这是可能的原因是
- 没有配置 transaction manager 实例,
- 没引入 aop 相关的依赖
- 如果是 spring boot 项目, 可能是
- 自定义了 trasaction manager, 但是没有在 @transaction 注解上配置manager 名字
- 编码上的写法错误
- 事务方法不是 public 的 (因为事务底层是动态代理, 非 public 方法无法被代理)
- 使用了 this 调用了事务方法, 即 this.xxxTransactionalMethod(...) , (this 是原始对象, 而不是生成的代理对象)
- 抛出的异常为 exception.class, 但是没有在 @trasactional 显式声明 rollbackfor (默认只 rollback runtime exception)
还可能异常被某个 aop 切面捕获了, 没法触发回滚
4. 同一个类中的方法嵌套调用: 如普通方法 a() call annotatied method B(), the transaction for B() will not trigger (this is also easy to explain: the calling to B() can be refered to as this.B(), which means the calling is not from a proxy object)
5. 多线程环境, 此时数据库连接都不是同一个, 肯定不在同一个事务了
// https://blog.csdn.net/laoxilaoxi_/article/details/99896738 使用 cglib or jdk 动态代理 `@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)// 使用cglib`
15.12.3. spring 事务传播失效的坑
// 事务传播
// 它们规定了事务方法和事务方法发生嵌套调用时是否加入调用方的事务
传播行为:一个业务 A (事务方法A),调用另一个业务 B (带有事务),B是否加入 A 的事务
- `PROPAGATION_REQUIRED` required 必须 (默认值)
如果 A 使用事务,那么 B 使用同一个事务 (此时 B 的事务配置都无效, 被 A 的事务覆盖了)。如果 A 没有事务,B 创建一个新的事务。
- `PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW` requires new 必须新的
无论 a 是否存在事务, b 都将创建新的事务 (小心死锁)
- `PROPAGATION_NESTED` nested 嵌套
AB 使用嵌套事务,底层使用 Savepoint, A 有事务, B 就创建一个子事务, A 没事务 , B 就创建个新事务
- PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS supports 支持
A 如果使用事务,B 使用同一个事务。A 没有事务,B 也就没有事务, 将以非事务执行
- PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED not supported 不支持
无论 a 是否存在事务, b 都以非事务执行 (若 A 有事务, 会暂时挂起该事物)
- PROPAGATION_NEVER never 从不
A 使用事务,B 将抛异常。A 没有事务,B 将以非事务执行
- PROPAGATION_MANDATORY mandatory 强制 (狗都不用)
A 使用事务,B 使用同一个事务。A 没有事务,B 抛出异常
同一个 service bean 中的 事务方法互相调用, 如 a() 调用 b(), 只会使用 a() 的 事务, b 的无效, 因为事务本质是基于动态代理, 在同个 bean 中的方法互调, 发生在主动调用方 a() 的代理对象中, 所以只有 a() 的事务生效
解决:
如果 a(), b() 处于不同 service bean 中, 则 事务传播生效.
或者
引入 starter aop, 会引入 aspectJ, @enableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy=true) 开启 aspectJ 并暴露代理对象, 在互调的部分, 使用代理对象互调
public void a() {
// b()
// c()
OrderService thisService = (OrderService) Aopcontext.currentProxy()
thisService.b()
thisService.c()
}
15.12.4. 避免长事务
避免长事务最简单的方法就是不要使用声明式事务@Transactional,而是使用编程式事务手动控制事务的颗粒度, 将不需要事务的逻辑移动到事务外面
如果使用了声明式事务, 在普通方法中调用事务方法, 要避免事务失效, 需要获取代理后的对象来调用事务方法
@Service
public class ArtisanService{
public void create(ArtisanDto dto){
queryData(); // 无需事务的逻辑
biz(); // 无需事务的逻辑
save(dto); // 错误, 因为是使用 this 调用的方法, 不是代理对象
// 方式 1: 将 事务方法放到另一个事务类, 在这里注入后调用 (注入的是代理后的类)
// 方式 2: 开启 AspectJ 字节码织入切面, @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true),方法内使用AopContext.currentProxy()获得代理类
}
//事务操作
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Throwable.class)
public void save(ArtisanDto dto){
artisanDao.insert(dto);
}
}
15.12.5. Transactional 注解
事务超时
@transaction(timeout=...) unit: s
隔离级别
@transaction(isolation=...)
15.13. 缓存
15.13.1. springboot-starter-cache
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置文件中配置类型为 redis: spring.cache.type: redis
注解:
- @cacheable({"xxxCache"}, sync=true) 缓存数据, 方法上, 指定缓存分区, sync 加锁防止缓存击穿
标注在方法 or 类上
标记在方法上 - 表示该方法是支持缓存的, 触发缓存读取操作
标记在类上 - 表示该类所有的方法都是支持缓存的
注解属性:
value/cachenames - 缓存名称(命名空间, 就是存入那块缓存), 只有这个是必须设置的
如果不生效, 可能是:
被缓存方法和调用者在同个类里面, 此时动态代理失效, 可引入 aop, 通过 aopcontext.currentproxy() 获取当前类的代理对象调用缓存方法, 参见 上一节 事务失效
- @cacheEvic(value="xxx", allEntries=true) 删除缓存, allEntries 表示删除分区 cache 下的全部缓存对
标注在方法或类上, 被标注的方法(类中的方法)的执行都会触发缓存的清除操作
注解属性:
allEntries -
@CacheEvict(value="accountCache",allEntries=true) 方法执行后清所有缓存
beforeInvocation
@CacheEvict(value="accountCache",beforeInvocation=true) 方法调用前清空所有缓存
- @cacheput 更新
标注在方法上, 触发缓存更新操作
- caching 组合多个操作
使用在 method or class 上, 综合上面的各种操作,(在有些场景下 ,调用业务会触发多种缓存操作)
- @cacheconfig 在类级别共享缓存配置
用在类上可以设置当前缓存的一些公共设置
- @enablecaching 开启缓存
自定义配置
// 自定义缓存 key
// 自定义 json 序列化, 不用默认的 jdk 序列化
// 自定义过期时间, 默认-1 永不过期
对于读模式:
- 缓存穿透 (查询一个 null 数据), 配置 cache-null-value=true 缓存 null 数据
- 缓存击穿 (大量并发同时请求一个快过期的key):
- 雪崩(大量key 同时过期), 配置 time-to-live 过期时间,
对于写模式: 没有很好的内置解决方法, 可以通过:
- 读写加锁
- canal 中间件
15.13.2. caffeine
Caffeine是使用Java8对Guava缓存的重写版本,在Spring Boot 2.0中将取代Guava
15.14. 配合 h2 数据库进行开发
15.14.1. h2 和 spring data jpa 配合
无需任何配置文件
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient // compared with @EnableEurekaClient, more comprehensive
public class ReservationServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ReservationServiceApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner initData(ReservationRepository reservationRepository) {
return args -> {
Stream.of("ehllo", "hello", "llhoe", "jojo", "猕猴桃")
.forEach(name -> reservationRepository.save(new Reservation(null, name)));
reservationRepository.findAll().forEach(System.out::println);
};
}
}
@RepositoryRestResource // publish repository as rest service
// 比如查询所有 /reservations, 查某个 /reservations/1, 搜索 /reservations/search ...
interface ReservationRepository extends JpaRepository<Reservation, Long> {
/**
* customized rest service
*
* http://localhost:8080/reservations/search/by-name?name=hello
*/
@RestResource(path = "by-name")
Optional<Reservation> findByName(String name);
}
@RestController
@RefreshScope
class ConfigRefreshTestController {
private final String message;
private final DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
public ConfigRefreshTestController(@Value("${message: defaultMsg}") String message,
@Autowired DiscoveryClient discoveryClient) {
this.message = message;
this.discoveryClient = discoveryClient;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/message", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String readMessage() {
return this.message;
}
@RequestMapping("/eureka-services")
public ResponseEntity<List<String>> eurekaServices() {
return new ResponseEntity<>(discoveryClient.getServices(), HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
/**
* entity: 预定
*/
@Entity
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor // if removed, jpa error may be produced
class Reservation {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
}
15.14.2. 和 mybatis-plus 配合
# DataSource Config
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
schema: classpath:db/schema-h2.sql
data: classpath:db/data-h2.sql
url: jdbc:h2:mem:test
username: root
password: test
@MapperScan("mapper package")
mapper extends BaseMapper
15.15. 多数据源
15.15.1. 基本配置 全注解开发
启动类需要排除自动配置@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
server.port=8335
# 配置第一个数据源
spring.datasource.hikari.db1.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/erp?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.hikari.db1.username=root
spring.datasource.hikari.db1.password=153963
spring.datasource.hikari.db1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# 配置第二个数据源
spring.datasource.hikari.db2.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/erp2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.hikari.db2.username=root
spring.datasource.hikari.db2.password=153963
spring.datasource.hikari.db2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "top.snailclimb.db1.dao", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "db1SqlSessionTemplate")
public class DataSource1Config {
/**
* 生成数据源. @Primary 注解声明为默认数据源
*/
@Bean(name = "db1DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.hikari.db1")
@Primary // 声明为默认数据源, 防止 dao 层的类忘记指定 @Qualifier("db1SqlSessionTemplate"), 可以使用默认的
public DataSource testDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 创建 SqlSessionFactory
*/
@Bean(name = "db1SqlSessionFactory")
@Primary
public SqlSessionFactory testSqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("db1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 若有 mapper.xml , 需要指定位置
// 若是全注解开发, 无需指定
// bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mybatis/mapper/db1/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
/**
* 配置事务管理
*/
@Bean(name = "db1TransactionManager")
@Primary
public DataSourceTransactionManager testTransactionManager(@Qualifier("db1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
/**
SqlSessionTemplate是线程安全的,可以被多个DAO所共享使用。
*/
@Bean(name = "db1SqlSessionTemplate")
@Primary
public SqlSessionTemplate testSqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("db1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "top.snailclimb.db2.dao", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "db2SqlSessionTemplate")
public class DataSource2Config {
@Bean(name = "db2DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.hikari.db2")
public DataSource testDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "db2SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory testSqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("db2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
//bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mybatis/mapper/db2/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean(name = "db2TransactionManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager testTransactionManager(@Qualifier("db2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "db2SqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate testSqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("db2SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
dao 开发:
@Qualifier("db1SqlSessionTemplate")
public interface UserDao {
/**
* 通过名字查询用户信息
mybatis中#{}和${}符号的区别
使用#{}意味着使用的预编译的语句,即 preparedStatement, 替换占位符时, 会为参数添加引号作为 string 传入, 防止注入攻击
也不是说${}一无是处,比如在MyBatis动态排序时使用order by +${动态参数},使用${}而不是#{}, 动态参数可以传入不定个数的字段.
*/
@Select("SELECT * FROM user WHERE name = #{name}")
User findUserByName(String name);
}
@Qualifier("db2SqlSessionTemplate")
public interface MoneyDao {
/**
* 通过id 查看工资详情
*/
@Select("SELECT * FROM money WHERE id = #{id}")
Money findMoneyById(@Param("id") int id);
}
15.15.2. AbstractRoutingDataSource 动态数据源切换
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37502106/article/details/91044952 https://www.cnblogs.com/wyb628/p/7240061.html
15.16. 多数据库类型 databaseIdProvider
https://www.cnblogs.com/valten/p/12083128.html# 配置 MySQL Oracle 共同使用
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Value("${mybatis.mapper-locations}")
private String mapperLocations;
@Primary
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.hikari")
public DataSource dataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate() {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource());
}
//如果配置了 databaseIdProvider,MyBatis 会加载所有的不带 databaseId 或匹配当前 databaseId 的语句;
// databaseId 是 mybatis 的内置参数
//如果带或者不带的语句都有,则不带的会被忽略。新增,修改和删除都有这个属性
/**
<!-- mybatis动态sql的两个内置参数 , 可以直接在 mapper.xml 中使用
_parameter:代表整个参数
单个参数:_parameter就是这个参数
多个参数:参数会被封装为一个map:_parameter就是代表这个map
_databaseId:如果配置了databaseIdProvider标签
_databaseId 就是代表当前数据库的别名Oracle
-->
<!-- List<Employee> getEmpsTestInnerParameter(Employee employee); -->
<select id="getEmpsTestInnerParameter" resultType="com.hand.mybatis.bean.Employee">
SELECT * FROM emp
<if test="_parameter!=null"> _parameter相当于传入的参数employee,判断employee是否为空,若不为空则执行where条件
where ename=#{_parameter.eName}
</if>
</select>
*/
@Bean
public DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider() {
DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider = new VendorDatabaseIdProvider();
Properties p = new Properties();
p.setProperty("Oracle", "oracle");
p.setProperty("MySQL", "mysql");
p.setProperty("PostgreSQL", "postgresql");
p.setProperty("DB2", "db2");
p.setProperty("SQL Server", "sqlserver");
databaseIdProvider.setProperties(p);
return databaseIdProvider;
}
@Primary
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(@Qualifier("dataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
factoryBean.setDatabaseIdProvider(databaseIdProvider());
factoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(mapperLocations));
return factoryBean;
}
}
# application.yml
# 切换对应的环境 postgresql mysql
spring:
profiles:
active: postgresql
# mybatis配置
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/**/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.valten.**.model
# showSql 控制台打印sql日志
logging:
level:
com:
valten:
dao: debug
---
# application-mysql.yml#
# 端口
server:
port: 8001
# 数据源配置
spring:
datasource:
hikari:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?&useSSL=false
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 123456
---
# application-postgresql.yml#
# 端口
server:
port: 8002
# 数据源配置
spring:
datasource:
hikari:
jdbc-url: jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/test
driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
username: root
password: 123456
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--oracle-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--postgresql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<version>9.4.1212</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 集成mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--fastjson-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.16</version>
</dependency>
<!-- druid数据库连接池组件 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
15.17. spring kafka
https://docs.spring.io/spring-kafka/docs/current/reference/html/#receiving-messages
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SqVfCyfCJqw&t=9s
16. web 相关
16.1. 加解密
https://github.com/Licoy/encrypt-body-spring-boot-starter web 层加密解密 加解密
https://github.com/yinjihuan/monkey-api-encrypt api 加解密
https://www.baeldung.com/java-aes-encryption-decryption 加密科普
https://www.cnblogs.com/loong-hon/p/11225407.html
https://www.javatt.com/p/22814 https://blog.csdn.net/github_36086968/article/details/103424945 https://jueee.github.io/2021/01/2021-01-06-SpringBoot%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0API%E6%8E%A5%E5%8F%A3%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AEAES%E5%8A%A0%E5%AF%86/
16.2. springboot 发送 https 或者 http 客户端 client
https://blog.csdn.net/defonds/article/details/86594441 (https://prasans.info/making-https-call-using-apache-httpclient/) https://www.cnblogs.com/lfstudy/p/13793625.html https://www.cnblogs.com/dbei/articles/12746191.html https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000014456939 使用 resttemplate
https://square.github.io/okhttp/ https://square.github.io/okhttp/https/
支持异步回调 Retrofit: https://www.jianshu.com/p/4d67fe493ebf https://www.zhihu.com/question/36963964 https://www.jianshu.com/p/5bc866b9cbb9
16.2.1. 发送 http client
16.2.2. 发送 https client
okhttp
@Configuration
public class JavaConfig {
@Bean(name = "myRestTemplate")
public RestTemplate restTemplate() throws KeyStoreException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, KeyManagementException {
TrustStrategy acceptingTrustStrategy = (X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) -> true;
SSLContext sslContext = org.apache.http.ssl.SSLContexts.custom()
.loadTrustMaterial(null, acceptingTrustStrategy)
.build();
SSLConnectionSocketFactory csf = new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(sslContext);
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
.setSSLSocketFactory(csf)
.build();
HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory =
new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory();
requestFactory.setHttpClient(httpClient);
//60s
requestFactory.setConnectTimeout(60 * 1000);
requestFactory.setReadTimeout(60 * 1000);
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(requestFactory);
restTemplate.getMessageConverters().set(1, new StringHttpMessageConverter(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
return restTemplate;
}
}
16.3. RequestContextHolder
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder
.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
16.4. 解决 api 版本共存
https://blog.csdn.net/j903829182/article/details/81836551, https://www.cnblogs.com/huanshilang/p/12097048.html 放在 url TODO
16.4.1. RequestMappingHandlerMapping
16.4.2. request matcher
private RequestMatcher matcherHtml = new AntPathRequestMatcher("/**", "GET");
把ServletRequest转化成HttpServletRequest,强转即可
调用matches方法进行匹配 boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request)
16.4.3. request condition
在 spring mvc 中,通过DispatchServlet接收客户端发起的一个请求之后,会通过 HanderMapping 来获取对应的请求处理器;而 HanderMapping 如何找到可以处理这个请求的处理器呢,这就需要 RequestCondition 来决定了
最终的实现类可能是针对以下情况之一:路径匹配,头部匹配,请求参数匹配,可产生MIME匹配,可消费MIME匹配,请求方法匹配,或者是以上各种情况的匹配条件的一个组合
public interface RequestCondition<T> {
// 一个http接口上有多个条件规则时,用于合并
//比如类上指定了@RequestMapping的 url 为 root - 而方法上指定的@RequestMapping的 url 为 method - 那么在获取这个接口的 url 匹配规则时,类上扫描一次,方法上扫描一次,这个时候就需要把这两个合并成一个,表示这个接口匹配root/method
T combine(T other);
// 判断是否成功,失败返回 null;否则,则返回匹配成功的条件
// 举个例子来讲,如果当前请求匹配条件是一个路径匹配条件,包含多个路径匹配模板,
// 并且其中有些模板和指定请求request匹配,那么返回的新建的请求匹配条件将仅仅
// 包含和指定请求request匹配的那些路径模板。
@Nullable
T getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request);
// 多个都满足条件时,用来指定具体选择哪一个。
int compareTo(T other, HttpServletRequest request);
}
AbstractRequestCondition 实现了equals,hashCode和toString 通用方法, 还通过protected抽象方法约定了实现类其他的一些内部通用逻辑
具体实现类:
- PatternsRequestCondition 路径匹配条件
- RequestMethodsRequestCondition 请求方法(get post delete..)匹配条件
- ParamsRequestCondition 请求参数匹配条件
- HeadersRequestCondition 头部信息匹配条件
- ConsumesRequestCondition 可消费MIME匹配条件
- ProducesRequestCondition 可生成MIME匹配条件
http文件传输操作
// springboot 原生 文件下载
@GetMapping("/download")
public ResponseEntity<Resource> download(HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse,
@RequestParam("id") String objId) throws Exception {
final MongoSysFileServiceImpl.DownloadFileVo downloadFileVo = sysFileService.downloadFile(objId);
if (downloadFileVo == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("指定文件不存在, objId = " + objId);
}
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.contentType(MediaType.parseMediaType("application/octet-stream"))
.header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION, "attachment; filename=\"" + downloadFileVo.getFilename() + "\"")
.body(new InputStreamResource(downloadFileVo.getIs()));
}
//上传
@PostMapping(value = "upload")
public R<SysFile> upload(@RequestPart("file") MultipartFile file)
{
try
{
// 上传并返回访问地址
final MongoSysFileServiceImpl.UploadFileResp uploadFileResp = sysFileService.uploadFile(file);
SysFile sysFile = new SysFile();
sysFile.setObjId(uploadFileResp.getObjId());
sysFile.setName(uploadFileResp.getGeneratedName());
return R.ok(sysFile);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
log.error("上传文件失败", e);
return R.fail(e.getMessage());
}
}
//feign client 远程调用
@PostMapping(value = "/upload", consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE)
public R<SysFile> upload(@RequestPart(value = "file") MultipartFile file);
// 传递 文件 , 同时传递请求参数
@PostMapping("/add")
public AjaxResult add( EstimateFile estimateFile, @RequestPart("files") MultipartFile[] files)
{ //@RequestPart("estimateFile")
return toAjax(estimateFileService.insertEstimateFile(estimateFile, files));
}
16.5. 接收参数相关的注解
//
// https://blog.csdn.net/u012894692/article/details/115875674
@RequestParam 可以用于从query parameters, form data, 和parts in multipart requests中获取参数。
即GET请求和POST(application/x-www-form-urlencoded ,multipart/form-data)请求的参数都可以使用@RequestParam
@RequestPart 用在multipart/form-data表单提交请求的方法上,支持的请求方法的方式MultipartFile,属于Spring的MultipartResolver类。
// 前三种支持 application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8’ 格式 (表单提交), 是浏览器默认的编码格式。
//
// multipart/form-data 格式 区别: 不会对参数编码,使用的boundary(分割线),相当于&,boundary的值是----Web**AJv3。 文件上传必须要这种格式, 也可用于键值对参数,最后连接成一串字符传输 (ref: https://www.jianshu.com/p/53b5bd0f1d44)
//
// @requestParam 注解方法参数, 可省略, 可以有多个
@ApiOperation("查询用户")
@PostMapping("/detailByParam")
public void detailByParam(@RequestParam (value = "id") Integer id,@RequestParam(value = "roleName") String roleName,@RequestParam(value = "roleDes") String roleDes) {
System.out.println(">>>id="+id+",roleName="+roleName+",roleDes="+roleDes);
// >>>id=1,roleName=admin,roleDes=拥有admin权限
}
@ApiOperation("查询用户")
@PostMapping("/detailByParam")
public void detailByParam(@RequestParam Map<String, String> params) {
System.out.println(">>>id="+params.get("id")+",roleName="+params.get("roleName")+",roleDes="+params.get("roleDes"));
// >>>id=1,roleName=admin,roleDes=拥有admin权限
}
@ApiOperation("查询用户")
@PostMapping("/detailByParam")
public void detailByParam(@RequestBody String params) {
System.out.println(">>>"+params);
// >>>id=1&roleName=admin&roleDes=%E6%8B%A5%E6%9C%89admin%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90
//
// 参数用 & 隔离开, 对于Get请求,是将参数转换?key=value&key=value格式,连接到url后
// 如果参数值中需要&,则必须对其进行编码。编码格式就是application/x-www-form-urlencoded(将键值对的参数用&连接起来,如果有空格,将空格转换为+加号;有特殊符号,将特殊符号转换为ASCII HEX值)
}
// 仅支持 application/json 格式, 不支持 application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8’
@ApiOperation("查询用户")
@PostMapping("/detailByParam")
public void detailByParam(@RequestBody GetRoleParam getRoleParam) {// @RequestBody 注解参数, 不可省略, 最多只能一个
System.out.println(">>>"+getRoleParam);
}
16.6. 自定义接收参数类型
若果只是一个两个类型需要转换, 直接实现 org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter 然后标注 component 即可 (包含连个泛型, 第一个是请求中原始类型如 Integer, 第二个泛型是 希望转换后的类型如 enum),
对 get/post 请求都有效
// 例子
@Component
public class StringToDateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {
private SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
@Override
public Date convert(String s) {
Date parse = null;
try {
parse = simpleDateFormat.parse(s);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return parse;
}
}
// 实例案例: 枚举转换
@Data
public class QueryRequest {
private GenderEnum gender;
}
@GetMapping("/get")//gender 只能接收到 MALE 、FEMALE 这样的参数,除此以外,均会报类型不匹配的错误信息,此时是无法处理 0 、1 这样的参数的
public Dict testGet(QueryRequest request) {
log.info("【get-request】= {}", JSONUtil.toJsonStr(request));
return Dict.create().set("get-request", request);
}
@PostMapping("/post")
public Dict testPost(@RequestBody QueryRequest request) {
log.info("【post-request】= {}", JSONUtil.toJsonStr(request));
return Dict.create().set("post-request", request);
}
// 增加一个转换器即可
@component
public class IntegerCodeToGenderEnumConverter implements Converter<Integer, GenderEnum> {
private Map<Integer, GenderEnum> enumMap = Maps.newHashMap();
public IntegerCodeToGenderEnumConverter() {
for (GenderEnum genderEnum : GenderEnum.values()) {
enumMap.put(genderEnum.getCode(), genderEnum);
}
}
@Override
public GenderEnum convert(Integer source) {
GenderEnum genderEnum = enumMap.get(source);
if (ObjectUtil.isNull(genderEnum)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("无法匹配对应的枚举类型");
}
return genderEnum;
}
}
当我们的枚举类特别多的时候, 不使用上面直接使用 Converter 的这种方法,我们引入 ConverterFactory 来解决这个问题
//通用枚举接口
public interface BaseEnum {
/**
* 获取枚举编码
*
* @return 编码
*/
Integer getCode();
}
@Getter
public enum GenderEnum implements BaseEnum {
/**
* 男
*/
MALE(0),
/**
* 女
*/
FEMALE(1);
/**
* 性别编码
*/
private Integer code;
GenderEnum(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
}
public class IntegerToEnumConverter<T extends BaseEnum> implements Converter<Integer, T> {
private Map<Integer, T> enumMap = Maps.newHashMap();
public IntegerToEnumConverter(Class<T> enumType) {
T[] enums = enumType.getEnumConstants();
for (T e : enums) {
enumMap.put(e.getCode(), e);
}
}
@Override
public T convert(Integer source) {
T t = enumMap.get(source);
if (ObjectUtil.isNull(t)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("无法匹配对应的枚举类型");
}
return t;
}
}
//创建对应的自定义 ConverterFactory 工厂类
public class IntegerCodeToEnumConverterFactory implements ConverterFactory<Integer, BaseEnum> {
private static final Map<Class, Converter> CONVERTERS = Maps.newHashMap();
/**
* 获取一个从 Integer 转化为 T 的转换器,T 是一个泛型,有多个实现
*
* @param targetType 转换后的类型
* @return 返回一个转化器
*/
@Override
public <T extends BaseEnum> Converter<Integer, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType) {
Converter<Integer, T> converter = CONVERTERS.get(targetType);
if (converter == null) {
converter = new IntegerToEnumConverter<>(targetType);
CONVERTERS.put(targetType, converter);
}
return converter;
}
}
// 注册工厂
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* 枚举类的转换器工厂 addConverterFactory
*/
@Override
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
registry.addConverterFactory(new IntegerCodeToEnumConverterFactory());
registry.addConverterFactory(new StringCodeToEnumConverterFactory());
}
}
16.7. 返回图片
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/image")
public class ImageController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/get")
@ResponseBody
public void getImage(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/test.jpg");
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()];
response.setContentType("image/jpeg");
OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
out.write(result);
out.flush();
//关闭响应输出流
out.close();
}
}
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/image")
public class ImageController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/get",produces = MediaType.IMAGE_JPEG_VALUE) //如果是网页的话,produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML
@ResponseBody
public byte[] getImage() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/test.jpg");
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()];
inputStream.read(bytes, 0, inputStream.available());
return bytes;
}
}
16.8. rest api 文档
16.8.1. knife4j
16.8.2. springdoc-openapi
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-rest-openapi-documentation
16.8.3. swagger3
访问 /swagger-ui.html or /swagger-ui/index.html (springdoc.swagger-ui.path=/swagger-ui.html)
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
@EnableOpenApi
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"cn.ruiyeclub.dao"})
public class Swagger3Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Swagger3Application.class, args);
}
}
@Configuration
public class Swagger3Config {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.OAS_30)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withMethodAnnotation(ApiOperation.class))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build()
// 协议使用 http; 默认是 https
.protocols(Stream.of("http").collect(Collectors.toSet()));
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Swagger3接口文档")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
16.8.4. 集成swagger2
http://springfox.github.io/springfox/docs/snapshot/#springfox-spring-mvc-and-spring-boot
- swagger2配置类,和APP启动类同级,@Configuration,@EnableSwagger2
- 访问:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
- 配置mvc时候, 如果继承了WebMvcConfigurationSupport, 需要重新注入资源文件, 否则访问不到swagger-ui.html;(ref)
- 分环境开启
- 在配置类上标注 @Profile({"dev","test"})
- 或者 在new Docket里添加.Enable(true/false)方法
- springfox.documentation.swagger-ui.enabled=false 生产 env 下 close
<!-- 会引入 谷歌的 guava -->
<!-- 版本可省略 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2Config {
// 添加 swagger 静态资源处理
// 一般我们会设置 mvc 中, spring.resources.add-mappings=false, 对静态资源默认不处理, 这是需要为 swagger 添加例外 (还会设置 spring.mvc.throw-exception-if-no-handler-found=true 没找到 Handler时直接抛出异常)
// @Bean
// public WebMvcConfigurer swaggerPassConfigure() {
// return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
// @Override
// public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
// registry.addResourceHandler("swagger-ui.html")
// .addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "/static", "/public");
//
// registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
// .addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
// }
// };
// }
@Bean
public Docket api() {
ParameterBuilder ticketPar = new ParameterBuilder();
List<Parameter> pars = new ArrayList<>();
ticketPar.name("Access-Token").description("Rest接口权限认证token,无需鉴权可为空")
.modelRef(new ModelRef("string")).parameterType("header")
//header中的ticket参数非必填,传空也可以
.required(false).build();
//根据每个方法名也知道当前方法在设置什么参数
pars.add(ticketPar.build());
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
// 根据包名扫描controller
// 自行修改为自己的包路径
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.tgpms")) // 多包配置: https://www.jianshu.com/p/78309feb5d5a
// 扫描所有controller
// .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
// 指定扫描部分注解标注的 controller
// .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withMethodAnnotation(Api.class/ApiOperation.class))
.paths(PathSelectors.any()) // .paths() 这个是包路径下的路径,PathSelectors.any()是包下所有路径
.build()
// 全局设置请求参数
.globalOperationParameters(pars);
//生成全局通用参数
// private List<RequestParameter> getGlobalRequestParameters() {
// List<RequestParameter> parameters = new ArrayList<>();
// parameters.add(new RequestParameterBuilder()
// .name("appid")
// .description("平台id")
// .required(true)
// .in(ParameterType.QUERY)
// .query(q -> q.model(m -> m.scalarModel(ScalarType.STRING)))
// .required(false)
// .build());
// parameters.add(new RequestParameterBuilder()
// .name("udid")
// .description("设备的唯一id")
// .required(true)
// .in(ParameterType.QUERY)
// .query(q -> q.model(m -> m.scalarModel(ScalarType.STRING)))
// .required(false)
// .build());
// parameters.add(new RequestParameterBuilder()
// .name("version")
// .description("客户端的版本号")
// .required(true)
// .in(ParameterType.QUERY)
// .query(q -> q.model(m -> m.scalarModel(ScalarType.STRING)))
// .required(false)
// .build());
// return parameters;
// }
// //生成通用响应信息
// private List<Response> getGlobalResonseMessage() {
// List<Response> responseList = new ArrayList<>();
// responseList.add(new ResponseBuilder().code("404").description("找不到资源").build());
// return responseList;
// }
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("online exam by springboot")
.description("在线考试系统 by 梁山广 at 2020")
.termsOfServiceUrl("https://github.com/19920625lsg/spring-boot-online-exam")
.version("1.0")
.contact(new Contact("liangshanguang", "https://github.com/19920625lsg/spring-boot-online-exam", "liangshanguang2@gmail.com"))
.build();
}
}
@Api("测试用例1") on controller class,
@ApiOperation(value = "apiOperationSwaggerTest", notes = "apiOperationSwagger测试") on controller class method
@ApiParam(name = "id", value = "id入参", required = true) on method params
@ApiModel(description = "测试实体类", value = "测试实体类") on data model class
@ApiModelProperty(name = "userName", value = "用户名", required = false, exmaple = "小明") on data module class field
@ApiImplicitParams({@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "id入参", required = true, dataType = "Integer", paramType = "query"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "brand", value = "brand", required = true, dataType = "BRAND", paramType = "body")
}) on controller class method
@ApiImplicitParams:用在请求的方法上,表示一组参数说明
@ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
name:参数名
value:参数的汉字说明、解释
required:参数是否必须传
paramType:参数放在哪个地方
· header --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
· query --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
· path(用于restful接口)--> 请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
· body(不常用)
· form(不常用)
dataType:参数类型,默认String,其它值dataType="Integer"
defaultValue:参数的默认值
16.9. 过滤器 和 拦截器
16.9.1. 区别
servlet filter和spring mvc Interceptor区别:
Filter 是基于 函数回调的,而 Interceptor 则是基于 Java 反射 和 动态代理。
Filter 依赖于 Servlet 容器, 和servlet容器隔的近,而 Interceptor 依赖springmvc, 和应用隔的近, 在最里层。所以filter 先进入, 最后退出
Filter 对几乎 所有的请求 起作用,而 Interceptor 只对 Controller 请求起作用。
拦截器可以获取IOC容器中的各个bean,而过滤器就不行,这点很重要,在拦截器里注入一个service,可以调用业务逻辑。
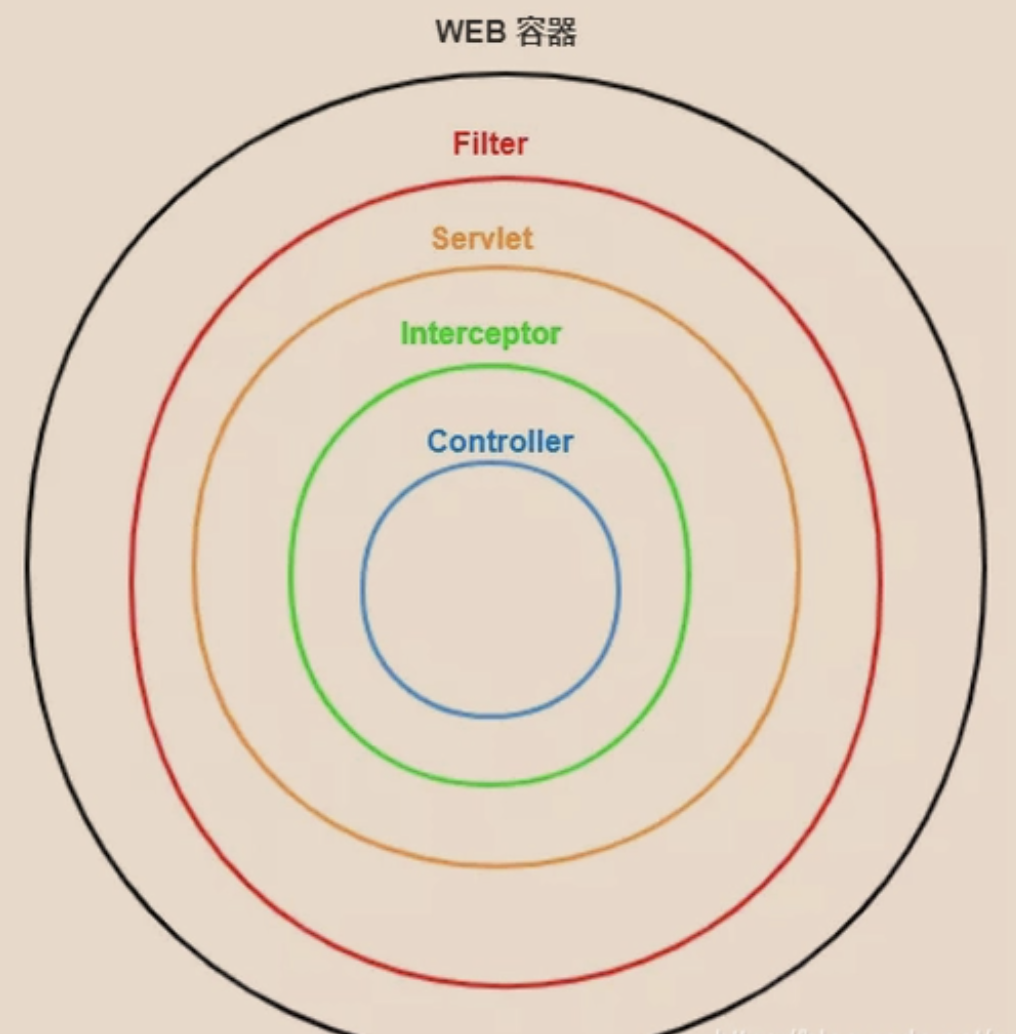
16.9.2. 使用 filter
scenario 1:
直接实现Filter接口,并使用@Component, 拦截所有路径 "/*", 这种方式可以注入 bean
scenario 2:
实现Filter接口,用@WebFilter注解,指定拦截路径以及一些参数,同时需要在启动类使用@ServletComponentScan扫描带@WebFilter、@WebServlet、@WebListener,
这种方式无法注入 bean, 除非 和 @component 一起使用, 但是需要配置覆盖 bean
#启用覆盖同名bean
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
scenario 3:
@Configuration
public class MyFilterConfig {
@Autowired
MyFilter myFilter;
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean<MyFilter> thirdFilter() { // 泛型指定 filter 类型, so 多个 filter 每个都要一个 bean 方法
FilterRegistrationBean<MyFilter> filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();
filterRegistrationBean.setOrder(2)
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(myFilter);
filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("/api/*")));
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
}
和 这里的 filter 不同, 这里是为了过滤 扫描
@ComponentScan(value="com.wxj",excludeFilters= {
@Filter(type=FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes= {Controller.class})
})
OncePerRequestFilter 被用于继承实现并在每次请求时只执行一次过滤
在Spring Security里面被广泛用到
和 Filter 有什么区别?
OncePerRequestFilter extends GenericFilterBean implements Filter{}, 只需要重写 Onecexxx.doFilterInternal(..)
- 请求发向 servlet 时会被 Filter 拦截,如果 servlet 将请求转发给另一个 servlet,请求发向第二个 servlet 时,依旧会被相同的 Filter 拦截。结果就是一个请求被同一个 Filter 拦截了两次。
- 而 OncePerRequestFilter 一个请求只被过滤器拦截一次。请求转发不会第二次触发过滤器。
16.9.3. 使用 interceptor
16.9.3.1. 基本使用拦截器
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-mvc-handlerinterceptor
实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口,
@component
class InterfaceAuthCheckInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
...
// 配置
@Configuration
public class InterceptorConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { // WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 过时, WebMvcConfigurationSupport, 对于 classpath:/META/resources/,classpath:/resources/,classpath:/static/,classpath:/public/)不生效, 所以选择WebMvcConfigurer 最好
@autowire
.... interceptor
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
// 多个拦截器组成一个拦截器链, 加入的顺序就是拦截器执行的顺序, 也可使用 @order(-1/0/1...)指定
// addPathPatterns 用于添加拦截规则, 默认拦截所有 即 /**
// excludePathPatterns 用户排除拦截
registry.addInterceptor(interceptor).addPathPatterns("/api/**").exclude("...");
}
16.9.3.2. 基于 url 拦截
一种方式是 在配置中 registry.addInterceptor(interceptor).addPathPatterns("/api/**").exclude("...");
一种是直接在 prehandle() 中处理 String path = request.getServletPath(), path.matches(Const.NO_INTERCEPTOR_PATH 就是基于正则匹配的url
16.9.3.3. 基于注解拦截
interceptor 也属于 aop,
public class AuthorityInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter{
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
// 如果不是映射到方法直接通过
if (!(handler instanceof HandlerMethod)) {
return true;
}
// ①:START 方法注解级拦截器
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();
// 判断接口是否需要登录
LoginRequired methodAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(LoginRequired.class);
// 有 @LoginRequired 注解,需要认证
if (methodAnnotation != null) {
// 这写你拦截需要干的事儿,比如取缓存,SESSION,权限判断等
System.out.println("====================================");
return true;
}
return true;
}
}
16.10. servlet Druid 监控
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource druid(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//配置Druid的监控
//1、配置一个管理后台的Servlet
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
Map<String,String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("loginUsername","admin");
initParams.put("loginPassword","123456");
initParams.put("allow","");//默认就是允许所有访问
initParams.put("deny","192.168.15.21");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
return bean;
}
//2、配置一个web监控的filter
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
Map<String,String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));
return bean;
}
}
16.11. aop 整合使用
16.11.1. 基本使用
通知执行顺序: around > before > around > after > afterReturning
// 只需要spring-boot-starter-aop
//@EnableAspectJAutoProxy// 无需, 自动开启,引入依赖后
@Component //必须
@Aspect
public class ReqCheckAop {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Pointcut("execution(org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<Resp> io.github.xiaoyureed.demo..*.*(..))")
private void pointcut() {}
@Around("pointcut()")
public Object reqCheck(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
System.out.println(">>> req = " + objectMapper.writeValueAsString(args[0]));
return jp.proceed();
}
}
16.11.2. 切入点表达式
用来指定增强哪些方法
https://www.cnblogs.com/ityangshuai/p/11923696.html
1.execution(xxx) 用于确定方法
表达式格式(就是方法签名):修饰符 返回值 包.类.方法(参数列表) throws 异常
1.1 修饰符 (可选),一般不使用 ----------- 接空格
public 公共修饰符
* 任意修饰符
1.2 返回值, 复杂类型需要全限定名称,常用 ----------- 接空格
String 返回字符串
* 返回任意
1.3 包 ,常用
com.xiaoyu.spring.learn.service 指定service包
com.xiaoyu.spring.learn.crm.*.service crm项目下的任意子模块(子文件夹)的service包
com.xiaoyu.spring.learn.service.. service目录包含的所有目录(包括次级子目录等等)
com.xiaoyu.spring.learn.crm.*.service.. crm下所有的子模块中service目录包含的所有目录
1.4 类,常用
UserService 指定类名
User* 以User开头类
*Service 以Service结尾类(常用)
* 任意类
1.5 方法,常用 与 1.4类相似
addUser 指定方法
add* add开头方法
*User 以User结尾方法
* 任意方法
1.6 参数列表,常用
() 没有参数
(int) 一个参数
(int,int) 两个参数
(..) 参数任意
1.7 异常 ,具体异常(可选)
多表达式:
<aop:pointcut experssion="exection(表达式1) || exection(表达式2) "> :表达式1或 表达式2
综合案例:execution(* com.xiaoyu.spring.learn.crm.*.service..*.*(..))
含义: 返回值任意,crm项目下的任意子目录中的的service目录下的所有目录中的任意类的任意方法,参数任意。
- within(): 只能指定 包.类; 再下面的粒度就没办法了, 所以相当于 execution() 的简化版
within(com.xiaoyu.spring.learn.aop..*)匹配aop 包/子包下的所有类的所有方法
指定注解类亦可
within(@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController *) 匹配 被 指定注解标注的所有类的所有方法
- this(): 用于向通知方法中传入代理对象的引用
如:
@Before("before() && this(proxy)")
public void beforeAdvide(JoinPoint point, Object proxy){
- target(): 用于向通知方法中传入目标对象的引用
- args() :用于将参数传入到通知方法中
如:
@Before("before() && args(age,username)")
public void beforeAdvide(JoinPoint point, int age, String username){
如
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.demo.aop.AopController.xxxMethod(int)) && args(point))") 会将拦截到的方法的 int 类型参数 传递到 aop 方法中, 使用 point 接受即可
-------
- @within :用于匹配在类一级使用了注解的类,其所有方法都将被匹配
@Pointcut("@within(com.cjm.annotation.AdviceAnnotation)") - 所有被@AdviceAnnotation标注的类都将匹配
常用:
@Pointcut("@annotation(AopLog) || @within(AopLog)") - 被 aopLog 标注的类 or 方法被拦截
- @target :和@within的功能类似,但必须要指定注解的保留策略为RUNTIME。
存疑?@target() 指定目标类型, 所有这个类型的类都会被匹配
@target(com.xiaoyu.spring.learn.aop.user.IUserDAO)匹配 IUserDAO 的所有实现类, 类中的方法都会被代理, 包括未在接口中声明的方法
- @args() 指定一个注解, 表示要拦截方法的参数需要带有这个注解
- @bean(id值) 对指定的目标对象的类进行匹配
- @annotation(参数中注解参数名称) 匹配被指定注解标注的方法
如: 下面表示 -> 匹配 web 包/子包下所有类的所有方法 且方法被 @CheckReqNo 标注
@Around("within(io.github.xiaoyureed.web..*) && @annotation(checkReqNo)")
public void xxx(JoinPoint jp, CheckReqNo checkReqNo)
- 可以使用 &&, ||, ! 运算符来定义切点表达式
16.12. controllerAdvice 使用
16.12.1. 全局异常处理 全局数据绑定 全局请求数据预处理
@ControllerAdvice //@ControllerAdvice注解 可以通过 assignableTypes 指定特定的类,让异常处理类只处理特定类抛出的异常
public class MyGlobalExceptionHandler {
// 直接返回 web 页面
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ModelAndView customException(Exception e) {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
mv.addObject("message", e.getMessage());
mv.setViewName("myerror");
return mv;
}
// 返回 json
@exception..
@respbody // 如果类上使用的是@RestControllerAdvice, 那么 返回 json 无需 @ResponseBody, 只需要 @ExceptionHandler
public respseentiyt xxx(Exception ex) {}
// 绑定 md 到每个 controler 中的方法参数中
@ModelAttribute(name = "md")
public Map<String,Object> mydata() {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("age", 99);
map.put("gender", "男");
return map;
}
// controller 中这么使用
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model) {// 或者 @ModelAttribute("md") Map<String, Object> md
Map<String, Object> map = model.asMap();
System.out.println(map);
int i = 1 / 0;
return "hello controller advice";
}
// 请求数据预处理
// 如此, 请求参数就可以传递这样的参数: a.name=xxx, b.name=yyy
// controller 中这样获取 @ModelAttribute("b") Book book, @ModelAttribute("a") Author author
@InitBinder("b")
public void b(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("b.");
}
@InitBinder("a")
public void a(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("a.");
}
}
处理异常的其他方法:
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)// 拦截所有异常
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> exceptionHandler(Exception e) {
if (e instanceof IllegalArgumentException) {
return ResponseEntity.status(400).body(illegalArgumentResponse);
} else if (e instanceof ResourceNotFoundException) {
return ResponseEntity.status(404).body(resourseNotFoundResponse);
}
return null;
}
@GetMapping("/resourceNotFoundException2")
public void throwException3() {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "Sorry, the resourse not found!", new ResourceNotFoundException());
}
16.13. 利用 ResponseBodyAdvice requestbodyadvice
16.13.1. 进行 feign 响应数据解包
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44817900/article/details/123035228 实现ResponseBodyAdvice接口,其实是对加了@RestController(也就是@Controller+@ResponseBody)注解的处理器将要返回的值进行增强处理。其实也就是采用了AOP的思想,对返回值进行一次修改。
https://www.cnblogs.com/melonOO/p/15349258.html
16.13.2. 请求响应加解密
https://www.jianshu.com/p/18f33cea8b8a
16.14. HttpServletRequest 的输入流只能读取一次的问题
https://www.cnblogs.com/JAYIT/p/10943155.html
还是推荐使用 aop 去切 controller 更方便一点
16.15. 路由处理
16.15.1. 静态资源映射 暴露静态资源
暴露图片资源
@Configuration
public class ImageConfig implements WebMvcConfigure {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/images/**") //addResourceLocations指的是文件放置的目录,addResoureHandler指的是对外暴露的访问路径
.addResourceLocations("file:./localdata/images/");
}
}
分环境暴露配置文件
// 配置文件访问地址 (注意每个访问路径后面的路径加 / !!!)
// ## windows系统下访问路径
// uploadWindow: E:\common\file\root\
// ## windows系统下访问路径
// uploadLinux: /user/img/
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
String os = System.getProperty("os.name");
//如果是Windows系统
if (os.toLowerCase().startsWith("win")) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/app_file/**")
// /app_file/**表示在磁盘filePathWindow目录下的所有资源会被解析为以下的路径
.addResourceLocations("file:" + filePathWindow);
} else { //linux 和mac
registry.addResourceHandler("/app_file/**")
.addResourceLocations("file:" + filePathLinux) ;
}
super.addResourceHandlers(registry);
}
还有个例子, --> swagger 静态资源处理 (放行 相关的静态页面)
16.15.2. 添加 view controller
@Configuration
class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* 添加 view controller
* <p>
* 将 url path 和 template 对应, 无需添加任何的 controller 代码
*/
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/home").setViewName("home");// 等价 访问 /home , controller 返回 "home"
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("home");
registry.addViewController("/hello").setViewName("hello");
registry.addViewController("/login").setViewName("login");
registry.addViewController("/admin-page").setViewName("admin-page");
}
}
16.16. spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
thymeleaf 和 spring security 配合使用 sec 标签: https://www.jianshu.com/p/bb3a3b388c4e
springboot默认 static/public 中放静态页面,而templates中放动态页面即 thymeleaf 模板
静态页面: 直接在static放一个hello.html,然后直接输入http://localhost:8080/hello.html 便能成功访问 (关闭这个特性需要 spring.resources.add-mappings: false), 也可以通过controller跳转 return "hello.html";
动态页面: 需要 spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf, 静态页面的return默认是跳转到/static/index.html,当在pom.xml中引入了thymeleaf组件,动态跳转会覆盖默认的静态跳转,默认就会跳转到/templates/index.html,注意看两者return代码也有区别,动态没有html后缀, 如果在使用动态页面时还想跳转到/static/index.html,可以使用重定向return "redirect:/index.html"
@RequestMapping("/Hi")
public String sayHello() {
return "hello";
}
@RequestMapping("/Hi")
public ModelAndView sayHello() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("hello");
modelAndView.addObject("key", 12345);
//System.out.println("test");
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping("/Hi")
public String sayHello(Map<String,obj> map) {
map.put("stu", new Stu())
return "hello";
}
配置:
#spring配置
spring:
mvc:
servlet:
load-on-startup: 1
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbootssm?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 123456
thymeleaf:
cache: false #关闭缓存
mode: HTML5 #设置模板类型
encoding: utf-8 #设置编码
prefix: classpath:/templates/
suffix: .html
content-type=text/html
17. 运维部署
17.1. 支持 https ssl
17.1.1. nginx 配置 https
Let's Encrypt 或者阿里云, 腾讯云 支持 面粉 ssl 证书 , 一年有效期, 过期再次申请
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000016760251 使用 lets encrypt 配置 nginx
https://www.cnblogs.com/to-red/p/12450616.html https://www.cnblogs.com/chnmig/p/10343890.html https://blog.csdn.net/fenglin0429/article/details/81347634 https://www.nonelonely.com/article/1584965619600 nginx 配置 http 转https, 代理 springboot https://ask.csdn.net/questions/701009
17.1.2. 支持 https 访问
// 假设如下的 api, 希望支持 https 访问, 现在仅仅只是http访问。http://localhost:8080
@RestController
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/",produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8")
String index(){
return "Hello Spring Boot!";
}
}
//生成ssl证书, 系统的当前用户目录下会生成一个keystore.p12文件, 将keystore.p12文件拷贝到我们项目的根路径下
// 1.-storetype 指定密钥仓库类型
// 2.-keyalg 生证书的算法名称,RSA是一种非对称加密算法
// 3.-keysize 证书大小
// 4.-keystore 生成的证书文件的存储路径
// 5.-validity 证书的有效期
keytool -genkey -alias tomcat -storetype PKCS12 -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -keystore keystore.p12 -validity 3650
// 修改配置文件
server.ssl.key-store=keystore.p12 //路径
server.ssl.key-store-password=123456 //生成ssl证书时设置的密钥库的口令
server.ssl.keyStoreType=PKCS12
server.ssl.keyAlias = tomcat
//此时工程已经支持https访问。 https://localhost:8080/
17.1.3. http 请求自动转为 https
// 配置访问http urL 时自动转到https。
// 配置后, 访问 https://localhost:8081/ 正常, 访问 http://localhost:8080/,我们可以看到页面的url变成了https://localhost:8081/
class Config {
@Bean
public EmbeddedServletContainerFactory servletContainer() {
TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory tomcat = new TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory() {
@Override
protected void postProcessContext(Context context) {
SecurityConstraint constraint = new SecurityConstraint();
constraint.setUserConstraint("CONFIDENTIAL");
SecurityCollection collection = new SecurityCollection();
collection.addPattern("/*");
constraint.addCollection(collection);
context.addConstraint(constraint);
}
};
tomcat.addAdditionalTomcatConnectors(httpConnector());
return tomcat;
}
@Bean
public Connector httpConnector() {
Connector connector = new Connector("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol");
connector.setScheme("http");
//Connector监听的http的端口号
connector.setPort(8080);
connector.setSecure(false);
//监听到http的端口号后转向到的https的端口号
connector.setRedirectPort(8081); // 需要设置 server.port=8081
return connector;
}
}
17.1.4. 同时支持 http https
用http请求时不再转换成https请求
只需要将代码中的connector.setSecure(false)中的false改成true就可以了
17.2. 容器化部署
https://rovo98.github.io/posts/39885a36/ SpringBoot + Docker + Nginx 负载均衡实现 TODO
https://github.com/GoogleContainerTools/jib 为 java 程序构造 docker 镜像 (https://www.cnblogs.com/felordcn/p/13201163.html)
17.3. nginx 反向代理
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1332603
17.4. 内嵌 tomcat 调优
server:
compression:
#SpringBoot 默认是不开启 gzip 压缩的,需要我们手动开启
enabled: true
#optional, 在 spring2.0+的版本中,默认值已经有了
mime-types: application/json,application/xml,text/html,text/plain,text/css,application/x-javascript
#默认情况下,仅会压缩 2048 字节以上的内容, 指定超过多少就压缩
min-response-size: 1024
tomcat:
# 排队数, 等待队列长度:队列做缓冲池用,但也不能无限长,消耗内存,出入队列也耗cpu
accept-count: 1000
max-connections: 10000 #最大可被连接数,默认为10000
#最大工作线程数, 默认 200
# 4核8G内存单进程调度线程数800-1000,超过这个并发数之后,将会花费巨大的时间在cpu调度上。
max-threads: 800
min-spare-threads: 100 #最小工作线程数, 默认 10
# 连接超时 30s
connection-timeout: 30000
# Maximum size, in bytes, of the HTTP message header
max-http-header-size:
# Maximum size, in bytes, of the HTTP post content.
max-http-post-size:
通过 java code 配置:
修改keepalivetimeout和maxKeepAliveRequests开启长连接
//当Spring容器内没有TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory这个bean时,会吧此bean加载进spring容器中
@Component
public class WebServerConfiguration implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableWebServerFactory> {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableWebServerFactory configurableWebServerFactory) {
//使用对应工厂类提供给我们的接口定制化我们的tomcat connector
((TomcatServletWebServerFactory)configurableWebServerFactory).addConnectorCustomizers(new TomcatConnectorCustomizer() {
@Override
public void customize(Connector connector) {
Http11NioProtocol protocol = (Http11NioProtocol) connector.getProtocolHandler();
//定制化keepalivetimeout,设置30秒内没有请求则服务端自动断开keepalive链接
protocol.setKeepAliveTimeout(30000);
//当客户端发送超过10000个请求则自动断开keepalive链接
protocol.setMaxKeepAliveRequests(10000);
// 设置其他....
}
});
}
}
// 或者这样配置, 效果等同
public class WebServerConfiguration {
@Bean
public ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory webServerFactory() {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
factory.setPort(11359);//端口号
factory.setUriEncoding(Charset.forName("utf-8"));//编码
factory.addConnectorCustomizers(new MyTomcatConnectorCustomizer());
return factory;
}
class MyTomcatConnectorCustomizer implements TomcatConnectorCustomizer {
@Override
public void customize(Connector connector) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Http11NioProtocol handler = (Http11NioProtocol)connector.getProtocolHandler();
handler.setAcceptCount(2000);//排队数
handler.setMaxConnections(5000);//最大连接数
handler.setMaxThreads(2000);//线程池的最大线程数
handler.setMinSpareThreads(100);//最小线程数
handler.setConnectionTimeout(30000);//超时时间
}
}
}
17.5. 配置 war 包部署到 Tomcat
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Application.class);
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses = Application.class, useDefaultFilters = true)
public class ServletContextConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport{
/**
* 配置servlet处理
*/
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
}
或者直接一步到位:
@SpringbootApplication
public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Application.class);
}
...
}
18. spring boot 中的并发
https://www.e4developer.com/2018/03/30/introduction-to-concurrency-in-spring-boot/ //todo https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40606397/article/details/104945855
18.1. 使用异步编程
18.1.1. 配置线程池
// 配置线程池
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfiguration {
@Bean("doSomethingExecutor")
public Executor doSomethingExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 核心线程数:线程池创建时候初始化的线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
// 最大线程数:线程池最大的线程数,只有在缓冲队列满了之后才会申请超过核心线程数的线程
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
// 缓冲队列:用来缓冲执行任务的队列
executor.setQueueCapacity(500);
// 允许线程的空闲时间60秒:当超过了核心线程之外的线程在空闲时间到达之后会被销毁
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
// 线程池名的前缀:设置好了之后可以方便我们定位处理任务所在的线程池
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("do-something-");
// 缓冲队列满了之后的拒绝策略:由调用线程处理(一般是主线程)
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
18.1.2. 有返回值 没有返回值
// 使用 没有返回值
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AsyncService {
// 指定使用beanname为doSomethingExecutor的线程池
@Async("doSomethingExecutor")
public String doSomething(String message) {
log.info("do something, message={}", message);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("do something error: ", e);
}
return message;
}
}
@RestController
public class AsyncController {
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/open/something")
public String something() {
int count = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
asyncService.doSomething("index = " + i);
}
return "success";
}
}
// 使用 有返回值
@RestController
public class AsyncController {
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
@SneakyThrows
@ApiOperation("异步 有返回值")
@GetMapping("/open/somethings")
public String somethings() {
CompletableFuture<String> createOrder = asyncService.doSomething1("create order");
CompletableFuture<String> reduceAccount = asyncService.doSomething2("reduce account");
CompletableFuture<String> saveLog = asyncService.doSomething3("save log");
// 等待所有任务都执行完
CompletableFuture.allOf(createOrder, reduceAccount, saveLog).join();
// 获取每个任务的返回结果
String result = createOrder.get() + reduceAccount.get() + saveLog.get();
return result;
}
}
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AsyncService {
@Async("doSomethingExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> doSomething1(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("do something1: {}", message);
Thread.sleep(1000);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("do something1: " + message);
}
@Async("doSomethingExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> doSomething2(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("do something2: {}", message);
Thread.sleep(1000);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("; do something2: " + message);
}
@Async("doSomethingExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> doSomething3(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("do something3: {}", message);
Thread.sleep(1000);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("; do something3: " + message);
}
}
18.1.3. @Async失效
- 异步方法使用static关键词修饰
- 异步类不是一个Spring容器的bean(一般使用注解@Component和@Service,并且能被Spring扫描到);
- SpringBoot应用中没有添加@EnableAsync注解;
- 在同一个类中,一个方法调用另外一个有@Async注解的方法,注解不会生效。原因是@Async注解的方法,是在代理类中执行的。
异步方法使用注解@Async的返回值只能为void或者Future及其子类,当返回结果为其他类型时,方法还是会异步执行,但是返回值都是null
19. 实现乐观锁悲观锁
https://www.cnblogs.com/cloudfloating/p/11461530.html
TODO
20. 移动端消息推送
https://juejin.im/post/6844903838495801357 https://crossoverjie.top/2018/09/25/netty/million-sms-push/ https://juejin.im/post/6844903478200909837 TODO
21. 即时通信 IM系统
22. 辅助工具
22.1. mapstruct
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<!-- <version>3.11.0</version>-->
<configuration>
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>1.5.5.Final</version>
</path>
<!-- working with lombok -->
<path>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
</path>
<path>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok-mapstruct-binding</artifactId>
<version>0.2.0</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
mapper 可以是 interface/Abstract class
// "public" is necessary
@Mapper
public interface SourceDestinationMapper {
SimpleDestination sourceToDest(SimpleSource source);
SimpleSource destToSource(SimpleDestination destination);
/**
* 字段名字不一样
*/
@Mapping(target="employeeId", source="entity.id")
@Mapping(target="employeeName", source="entity.name")
EmployeeDTO employeeToEmployeeDTO(Employee entity);
@Mapping(target="id", source="dto.employeeId")
@Mapping(target="name", source="dto.employeeName")
Employee employeeDTOtoEmployee(EmployeeDTO dto);
/**
* 内嵌对象也可以复制, 需要声明内嵌的对象转换方法, mapstruct 会自动调用
*/
/*
* 时间格式 (employeeStartDt 为 string 类型, startDt 为 date 类型)
*/
@Mapping(target="employeeStartDt", source = "entity.startDt",
dateFormat = "dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm:ss")
}
@Getter
@Setter
public static class SimpleSource {
private String name;
private String description;
// getters and setters
}
@Getter
@Setter
public static class SimpleDestination {
private String name;
private String description;
// getters and setters
}
使用
@Test
void mstest() {
// 也可以将这里放到 mapper interface 内, 使用时这样: Xxxmapper.mapper.xxx()
SourceDestinationMapper mapper = Mappers.getMapper(SourceDestinationMapper.class);
SimpleSource simpleSource = new SimpleSource();
simpleSource.setName("a");
simpleSource.setDescription("d");
SimpleDestination simpleDestination = mapper.sourceToDest(simpleSource);
assertThat(simpleDestination.getName()).isEqualTo("a");
assertThat(simpleDestination.getDescription()).isEqualTo("d");
}
在 map 前后, 做一些自定义处理:
@Mapper
public abstract class CarsMapper {
@BeforeMapping
protected void enrichDTOWithFuelType(Car car, @MappingTarget CarDTO carDto) {
if (car instanceof ElectricCar) {
carDto.setFuelType(FuelType.ELECTRIC);
}
if (car instanceof BioDieselCar) {
carDto.setFuelType(FuelType.BIO_DIESEL);
}
}
@AfterMapping
protected void convertNameToUpperCase(@MappingTarget CarDTO carDto) {
carDto.setName(carDto.getName().toUpperCase());
}
public abstract CarDTO toCarDto(Car car);
}
Copy
22.2. lombok notice
@data <=> @Setter、@Getter、@RequiredArgsConstructor、@ToString、@EqualsAndHashCode,
若存在继承, 需要为 son 指定 @EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
@RequiredArgsConstructor 表示为不可变 field 生成 constructor, 也就是为 final 的成员或者@notnull成员生成 constructor, 其他普通的 field 不会作为构造参数,
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName="of"), staticname=of 表示这个类不能用构造方法构造出来,必须通过 XxxClass.of(...)方法才能构造出来
推荐通用的组合是 @data, @all... , @no...
和 Java8 配合良好, jdk升级很麻烦, 需要 delombok
@builder 构造对象时底层用的是全参数构造器, 需要 @AllArgsConstructor一起用, 无法单独使用, 若果一定要用, 好的组合是 @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Builder @Data
- 推荐使用 @accesssor(chain=true), 注意Accessor 产生的方法和 cglib 冲突, 比如 beancopier.create() 就会报错, 此时可使用 spring 提供的 copy util (ref: https://github.com/cglib/cglib/issues/108)
代替@AutoWired注解: @RequiredArgsConstructor(onConstructor =@__(@Autowired))标注在类上, 那么注入成员的时候, 可以省掉 @autowired 注解 (会自动生成构造器)
替代@tostring注解 可以使用 lang3 的
ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(this)@value, 标注为不可变类 (final class, private final fields, only getter, no setter, all args contructor)
- 使用时, 类的 field 可以不带任何修饰符, 会自动被加上 private final
22.2.1. 编译期代码生成原理
https://www.cnblogs.com/exmyth/p/11396503.html
https://blog.csdn.net/Chinajash/article/details/1471081
https://www.baeldung.com/java-annotation-processing-builder
22.3. devtools
开发者组件, 修改了 thymeleaf 后, 重新编译修改的文件, 页面即可更新, 不必重启整个 app, 但是若修改了 Java config , 还是要重启
spring.thymeleaf.cache=true
spring.devtools.restart.enabled=true
... additional-paths=src/main/java // 监听目录
22.4. maven wrapper
wrapper:maven的包装器,通过mvnw命令替代mvn,简化mvn操作, 不需要在操作系统上安装Maven
受到 gradle wrappe 启发
/.mvn/wrapper/maven-wrapper.jar 是其主体程序
/.mvn/wrapper/maven-wrapper.properties 可指定 maven 版本及下载路径
mvnw, mvnw.cmd 命令行程序
mvnw第一次运行会检测$USER_HOME/.m2/wrapper/dists 目录下是否有maven-wrapper.properties中指定的Maven版本,如果没有就自动下载
23. 校验
23.1. 校验配置文件
任何添加@ConfigurationProperties的类,class上加 @Validated annotation, app都会进行属性校验, 确保引入了 JSR-303 javax.validation 规范的实现;
使用校验规范JSR-303 javax.validation中的注解即可实现校验(介绍见这里https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-jsr303/)
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="connection")
@Validated
public class FooProperties {
@NotNull
private InetAddress remoteAddress;
@Valid // 这里是为了激活 Security类中的注解校验
private final Security security = new Security();
// ... getters and setters
public static class Security {
@NotEmpty
public String username;
// ... getters and setters
}
}
@Validated 也可以可以加到 @Bean 方法上 来触发校验;
也可以使用自定的Spring Validator,bean id是 configurationPropertiesValidator 即可
spring-boot-actuator 模块有一个端点,对外暴露了所有的 @ConfigurationProperties beans。浏览器中访问 /configprops 即可
23.2. 校验请求参数
https://blog.csdn.net/mzh_cn/article/details/80637015
23.3. 自定义校验
23.4. @Validated和@Valid
@Valid是 JSR-303 规范, hibernate-validation实现了这一规范
@Validated来自于spring, 是 spring 对于 @Valid 的实现, 提供"validation groups"功能(创建空接口作为分组), valid则不具备;(https://stackoverflow.com/questions/36173332/difference-between-valid-and-validated-in-spring) , 一旦controler 中使用 @Validated(group={...}), 那么实体类字段上的注解若指定 group 则约束生效, 不指定分组的不生效. 反之, 若 @validated 没有指定分组, 则 实体类字段指定了 group 的不生效, 不指定group 的字段生效
24. runner 获取命令行参数
24.1. 获取命令行参数
注入一个org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments bean
@Component
public class MyBean {
@Autowired
public MyBean(ApplicationArguments args) {
boolean debug = args.containsOption("debug");//option参数即“--”开头的参数
List<String> files = args.getNonOptionArgs();// if run with "--debug logfile.txt" 那么结果是 debug=true, files=["logfile.txt"]
}
}
另外的注入方法:
Spring Boot will also register a CommandLinePropertySource with the Spring Environment. This allows you to also inject single application arguments using the @Value annotation.
24.2. ApplicationRunner or CommandLineRunner
ApplicationRunner or CommandLineRunner接口都有run()待实现(在SpringApplication.run(…)完成之前调用)但是参数不同, 具体如下:
ApplicationRunner接口,
void run(ApplicationArguments args)CommandLineRunner接口,
void run(String... args)
@Component
public class MyBean implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) {//可以获取命令行参数, 作为String[]
// 这里的内容会在app完全启动前最后一步执行, 即SpringApplication.run(…)完成之前, 也会在ApplicationReadyEvent之前
}
}
// 另一种方法:
//java -jar commandline-app-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar iamnonoption --app.name=CmdRulez --app.hosts=abc,def,ghi --app.name=2
implements ApplicationRunner
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
// 获取非 --xxx=yyy 的参数集合
System.out.println("# NonOptionArgs: " + args.getNonOptionArgs().size());
System.out.println("NonOptionArgs:");
args.getNonOptionArgs().forEach(System.out::println);
// 获取 --xxx=yy 的参数中的 key
System.out.println("# OptionArgs: " + args.getOptionNames().size());
System.out.println("OptionArgs:");
args.getOptionNames().forEach(optionName -> {
System.out.println(optionName + "=" + args.getOptionValues(optionName));// 获取 value
});
}
如果有多个CommandLineRunner or ApplicationRunner beans 被定义, 这时候涉及到调用数序问题, 两种方式:
实现
org.springframework.core.Ordered接口使用
org.springframework.core.annotation.Order注解 eg: @Order(num), num为Int, 0优先级最高
25. 开发命令行应用
加入开发一个工具 ab.jar, 希望这么使用:
- java -jar ab.jar 使用提示
- java -jar ab.jar --spring.profiles.active=hello-world,receiver 激活不同的 profile
配置中指定一个默认 激活 profile
spring:
profiles:
active: usage_message
// 工具使用提示
@Profile("usage_message")
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner usage() {
return args -> {
System.out.println("This app uses Spring Profiles to
control its behavior.\n");
System.out.println("Sample usage: java -jar
rabbit-tutorials.jar
--spring.profiles.active=hello-world,sender");
};
}
// 若出传递了参数, 则 usage_message 就被覆盖, 这个 bean 被注册
@Profile("!usage_message")
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner tutorial() {
return new RabbitAmqpTutorialsRunner();
}
// 传递不同的参数, 不同的 profile 会激活
@Profile("receiver")
@Bean
public Tut1Receiver receiver() {
return new Tut1Receiver();
}
@Profile("sender")
@Bean
public Tut1Sender sender() {
return new Tut1Sender();
}
// 具体操作
public class RabbitAmqpTutorialsRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Value("${tutorial.client.duration:0}")
private int duration;
@Autowired
private ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx;
@Override
public void run(String... arg0) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Ready ... running for " + duration + "ms");
Thread.sleep(duration);
ctx.close();
}
}
26. 整合 grpc
https://github.com/ChinaSilence/spring-boot-starter-grpc
27. 任务调度
27.1. 整合 XXL-JOB 任务调度平台
https://www.tianheyu.top/archives/springboot-xxl-job-executor
27.2. 异步任务
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//核心线程数
taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(8);
//最大线程数
taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(16);
//队列大小
taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(100);
// 当最大池已满时,此策略为我们提供可伸缩队列,此策略保证不会丢失任务请求,但是可能会影响应用程序整体性能。
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("My ThreadPoolTaskExecutor-");
taskExecutor.initialize();
return taskExecutor;
}
}
// 使用
@Service
public class FutureService {
//在需要执行的方法上加@Async表明该方法是个异步方法,如果加在类级别上,则表明类所有的方法都是异步方法
@Async
public Future<String> futureTest() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("任务执行开始,需要:1000ms");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println("do:" + i);
}
System.out.println("完成任务");
return new AsyncResult<>(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Async
public CompletableFuture<List<String>> completableFutureTask(String start) {
// 打印日志
logger.warn(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "start this task!");
// 找到特定字符/字符串开头的电影
List<String> results =
movies.stream().filter(movie -> movie.startsWith(start)).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 模拟这是一个耗时的任务
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回一个已经用给定值完成的新的CompletableFuture。
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(results);
}
}
27.3. 定时任务
27.3.1. springboot 内置
SpringBoot为我们内置了@Scheduled定时任务 (spring task), @EnableScheduling 开启
@Scheduled注解各参数详解: (https://www.jianshu.com/p/1defb0f22ed1)
- cron
- zone
- fixedDelay 上次完毕到下次开始(ms)
- fixedDelayString="${time.fixedDelay}" 同上
- fixedRate 上次开始到下次开始
- initialDelay 首次延迟
自定义线程池:
//默认情况下,@Scheduled任务都在Spring创建的大小为1的默认线程池中执行
@Configuration
public class SchedulerConfig implements SchedulingConfigurer {
private final int POOL_SIZE = 10;
@Override
public void configureTasks(ScheduledTaskRegistrar scheduledTaskRegistrar) {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolTaskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
threadPoolTaskScheduler.setPoolSize(POOL_SIZE);
threadPoolTaskScheduler.setThreadNamePrefix("my-scheduled-task-pool-");
threadPoolTaskScheduler.initialize();
scheduledTaskRegistrar.setTaskScheduler(threadPoolTaskScheduler);
}
}
27.3.2. 集成 Quartz
28. 配置文件 and 环境
28.1. 读取配置文件
28.1.1. 几种读取配置文件的方法
使用 @Value("${property}") 读取比较简单的配置信息
通过@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "library")读取并与 bean 绑定, 需要 加 @component(此时无需在配置类上添加 @EnableConfigurationProperties), 若不用 @component, 则必须 在任意一个配置类上添加 @EnableConfigurationProperties(...)
@ConfigurationProperties 配合 @bean 用在方法上, 方法调用空构造函数返回想要构造的对象
@PropertySource("classpath:website.properties") 读取指定 properties 文件
28.1.2. 注入复杂类型
对于 properties 格式的配置文件:
# application.properties
#
#单个值
val=10
# List
list=1,2,3,4
#Map
map={'name':'chen', 'age':'12', 'sex':'男'}
#java
# 用到了spel表达式
@PropertySource("classpath:xxx")
public class ConfigProps {
//单个数值,可注入为int或String
@Value("${val}")
private int val;
//array 数组
@Value("#{'${ips}'.split(',')}")
private List<String> iplist;
//map
@Value("#{${map}}")
private Map<String, String> map;
}
对于 yml 格式的文件:
custom:
ignored-token-path: /base/xx/login, /xx/**/, /xx/hfc/test
然和配置接受类
@Configuration // 也可以用 @component, 若果不想用这类注解, 可以去掉, 取而代之在启动类上标注 @enableConfigProperties(xxx.class), 相当于加了 @Component
@ConfigurationProperties("custom")
public class Custom {
private String[] ignoredTokenPath;
}
custom:
mail[0]:
username: xxx@xxx.com
password: axxx
mail[1]:
username: xxx@xxx.com
password: axxx
@component
@ConfigurationProperties("custom")
public class Custom {
private List<MailInfo> mail;
static class MailInfo {
private String username;
private String password;
}
}
directory:
maps:
11: /dciZhongShan/resourceWarn/agricultureLand
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "directory")
public class MapConfig {
private Map<Integer, String> maps;
}
28.2. 配置文件优先级
配置文件加载优先级: 命令行 > ${user.dir}/config/xxx > ${user.dir}/xxx (usr.dir 即为命令执行的当前目录) > classpath:config/xxx > classpath:xxx
--spring.profiles.active=prod,,,, --spring.config.location=target/application.properties
28.3. 读取环境信息
/**
* @author xiaoyu
* date: 2020/3/21
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootDemoApp {
/**
* springboot在启动的时候需要检测当前项目是否是一个web项目,
* 检测方式为判断classpath中是否有以下final变量中定义的两个参数
*/
private static final String[] WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES =
new String[]{"javax.servlet.Servlet", "org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext"};
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SpringbootDemoApp.class, args);
ConfigurableEnvironment env = context.getEnvironment();
String[] activeProfiles = env.getActiveProfiles();
String port = env.getProperty("server.port");
System.out.println("==============================");
System.out.println("active profiles: " + Arrays.toString(activeProfiles));
System.out.println("local uri: http://localhost:" + port);
System.out.println("local area network uri: http://" + localAreaNetwork() + ":" + port);
System.out.println("==============================");
}
private static String localAreaNetwork() {
try {
return InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "get local area network error";
}
}
private boolean deduceWebEnv() {
//https://blog.csdn.net/txba6868/article/details/80732475
return true;
}
}
@RestController
class DemoController {
/**
* file upload 文件上传
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/upload", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<String> upload(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
MultipartHttpServletRequest req = (MultipartHttpServletRequest) request;
MultipartFile aa = req.getFile("aa");
MultipartFile bb = req.getFile("bb");
aa.transferTo(Paths.get(System.getProperty("user.home") + "/tmp").toFile());
return ResponseEntity.ok("ok");
}
}
28.4. 两种引入 springboot 方式
一种是通过 设置 parent 为 spring boot starter parent
一种是通过 dependencyManagement 加入 spring boot dependencies (需要 设置 maven properties, maven.compiler.source 和 maven.compiler.target 防止编译使用 jdk 1.5)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<!-- <parent>-->
<!-- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>-->
<!-- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>-->
<!-- <version></version>-->
<!-- <relativePath/> <!– lookup parent from repository –>-->
<!-- </parent>-->
<groupId>io.github.xiaoyureed</groupId>
<artifactId>shopee</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<description>聚合服务</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<maven.compiler.source>${java.version}</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>${java.version}</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<spring-boot.version>2.3.4.RELEASE</spring-boot.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.SR8</spring-cloud.version>
<spring-cloud-alibaba.version>2.2.1.RELEASE</spring-cloud-alibaba.version>
<aliyun-spring-boot.version>1.0.0</aliyun-spring-boot.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-alibaba.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${aliyun-spring-boot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 代码生成 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId>
<version>3.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.velocity/velocity-engine-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity-engine-core</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.httpcomponents/httpcore -->
<!-- common module need this-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpcore</artifactId>
<version>4.4.13</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.commons/commons-lang3 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.11</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
使用这种方式 spring boot maven plugin 可能失效, 需要手动配置
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
29. 国际化 i18n
如果我们需要获取客户端的语言,本地化(国际化 i18n)参数,我们可以借助 Spring 提供的 LocaleContextHolder API 进行获取,比如: 1、获取语言:LocaleContextHolder.getLocale().getLanguage() 2、获取时区:LocaleContextHolder.getLocale().getTimeZone() 等等。
30. 序列化 反序列化
30.1. 日期时间 json
https://www.cnblogs.com/carrychan/p/9883172.html https://blog.csdn.net/z69183787/article/details/109356584
30.2. jackson 使用
springboot web starter 中包含了 Jackson-databind 依赖, 可以直接注入 objectmapper, 若自己定制:
30.2.1. @JsonComponent
用于对特定属性定制序列化
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Color favoriteColor;
}
@JsonComponent
public class UserCombinedSerializer {
public static class UserJsonSerializer // 若只需要序列化, 不需要反序列化, 则只需要这个类 并在这个类标注 @JsonComponent. 外层类和下面的内部类类都不需要,
extends JsonSerializer<User> {
@Override
public void serialize(User user, JsonGenerator jsonGenerator,
SerializerProvider serializerProvider) throws IOException,
JsonProcessingException {
jsonGenerator.writeStartObject();
jsonGenerator.writeStringField(
"favoriteColor", getColorAsWebColor(user.getFavoriteColor()));
// ... 其他属性...
jsonGenerator.writeEndObject();
}
private static String getColorAsWebColor(Color color) {
int r = (int) Math.round(color.getRed() * 255.0);
int g = (int) Math.round(color.getGreen() * 255.0);
int b = (int) Math.round(color.getBlue() * 255.0);
return String.format("#%02x%02x%02x", r, g, b);
}
}
public static class UserJsonDeserializer
extends JsonDeserializer<User> {
@Override
public User deserialize(JsonParser jsonParser,
DeserializationContext deserializationContext)
throws IOException, JsonProcessingException {
TreeNode treeNode = jsonParser.getCodec().readTree(jsonParser);
TextNode favoriteColor = (TextNode) treeNode.get(
"favoriteColor");
return new User(Color.web(favoriteColor.asText()));
}
}
}
30.2.2. Jackson 在 springboot 中的配置
spring.jackson.date-format指定日期格式,比如yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,或者具体的格式化类的全限定名
spring.jackson.deserialization是否开启Jackson的反序列化
spring.jackson.generator是否开启json的generators.
spring.jackson.joda-date-time-format指定Joda date/time的格式,比如yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss). 如果没有配置的话,dateformat会作为backup
spring.jackson.locale指定json使用的Locale.
spring.jackson.mapper是否开启Jackson通用的特性.
spring.jackson.parser是否开启jackson的parser特性.
spring.jackson.property-naming-strategy指定PropertyNamingStrategy(CAMEL_CASE_TO_LOWER_CASE_WITH_UNDERSCORES)或者指定PropertyNamingStrategy子类的全限定类名.
spring.jackson.serialization是否开启jackson的序列化.
spring.jackson.serialization-inclusion指定序列化时属性的inclusion方式,具体查看JsonInclude.Include枚举.
spring.jackson.time-zone指定日期格式化时区,比如America/Los_Angeles或者GMT+10
30.2.3. jackson注解
@JsonIgnore 此注解用于属性上,作用是进行JSON操作时忽略该属性。
@JsonIgnoreProperties(value = { "intValue" }) on type, 忽略指定属性
@JsonIgnoreType on type 忽略所有属性
//or @JsonIgnoreType on mixin type(empty type) to ignore fields of the type which we have no access to
// mapper.addMixIn(String[].class, MyMixInForIgnoreType.class);//MyMixInForIgnoreType is empty
//Note: Since version 2.5 – it seems that we can not use this method to ignore primitive data types, but we can use it for custom data types and arrays.
@JsonFormat 此注解用于属性上,作用是把Date类型直接转化为想要的格式,如@JsonFormat(pattern = “yyyy-MM-dd HH-mm-ss”)。
@JsonProperty 此注解用于属性上,作用是把该属性的名称序列化为另外一个名称,如把trueName属性序列化为name,@JsonProperty(“name”)。
@JsonValue 用于属性/get方法上, 一个类只能用一个, 相当于自定义序列化, 当加上@JsonValue注解,序列化是只返回这一个字段的值/方法的值作为当前对象的值
@JsonRawValue on json string field to serialize raw json string
30.2.4. objectmapper 定制
https://www.kancloud.cn/ahutchen/spring-boot-reference-guide/333370
@Bean
public ObjectMapper objectMapper() {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
/*
>>> serialization config
*/
//序列化的时候序列对象的所有属性
// JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL 忽略 null 值
// Include.NON_EMPTY 如果为null或者 空字符串和空集合都不会被序列化
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.ALWAYS);
//如果是空对象的时候,不抛异常
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false);
// 格式化输出
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.INDENT_OUTPUT, true);
//or
mapper.enable(SerializationFeature.INDENT_OUTPUT);
// 自定义时间格式
//取消时间的转化格式,默认是时间戳,可以取消,同时需要设置要表现的时间格式
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false);// 默认为true,会显示时间戳
objectMapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))
// config filter
//
// new SimpleBeanPropertyFilter.FilterExceptFilter()
// objectMapper.setFilterProvider()
/*
>>> deserialization config
*/
//反序列化的时候如果多了其他属性,不抛出异常
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
//@JsonValue 可以用在get方法或者属性字段上,一个类只能用一个,当加上@JsonValue注解是,序列化是只返回这一个字段的值
//@JsonRootName(value = "user") to wrapper a root property for output json
//@JsonSerialize(using = CustomDateSerializer.class) on field to specify a customized serializer
// ex: class CustomDateSerializer extends StdSerializer<Date>
return objectMapper;
}
30.2.5. objectmapper 使用
// >>> 序列化数组
Person person1 = new Person(1, "zxc", new Date());
Person person2 = new Person(2, "ldh", new Date());
List<Person> persons = new ArrayList<>();
persons.add(person1);
persons.add(person2);
String personStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(persons);
//反序列化为List<user> 集合,1需要通过 TypeReference 来具体传递值
List<Person> persons2 = objectMapper.readValue(personStr, new TypeReference<List<Person>>() {});
//or
//通过 JavaType 来进行处理返回
JavaType javaType = objectMapper.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(List.class, Person.class);
List<Person> persons3 = objectMapper.readValue(personStr, javaType);
31. 接入第三方支付
https://github.com/Javen205/IJPay
https://github.com/egzosn/pay-java-parent https://github.com/egzosn/pay-spring-boot-starter-parent
https://github.com/Pay-Group/best-pay-sdk
https://github.com/iyangyuan/pay-spring-boot
https://github.com/jeequan/jeepay
https://github.com/roncoo/roncoo-pay
https://github.com/Exrick/xpay 个人收款
32. 轻量级的技术栈
java8,guice,javalin(写 rest api),nashorn(js engine),arangodb (多模型数据库, 支持图,键值对,...)
32.1. dagger2 编译器依赖注入
There are many methods can be used to perform dependency injection, such as
constructor injection
setter method injection
for the two ways, there are too mach sacaffold code need devs to finish, but luckily, Spring framework helps the devs to handle these code. 但是这种运行时动态注入, 在 debug 是非常难以定位问题
For dagger2, it reach the goal by using annotation, and it works in the compiling duration
33. 拾遗
33.1. bean 懒加载
一般情况下,Spring容器在启动时会创建所有的Bean对象,使用@Lazy注解 (和 @Component 共同使用) 可以将Bean对象的创建延迟到第一次使用Bean的时候
33.2. bean 循环依赖
什么是循环依赖 ?
- 一个 bean 注入了自己的一个实例
- 两个 bean 互相注入 (spring 默认能解决)
- 多个 bean 注入, 形成环形
spring 通过 3 个 map 缓存解决
一级缓存: 存储完整构造后的bean 二级缓存: 存储刚刚创建还没填充属性的空 bean 三级缓存: 保存bean 的创建工厂 (空 bean 创建后, 会吧对应的 ObjectFactory 存到这里, 叫做提前暴露)
对于情况 2, 注入流程如下:
a 依赖 b, b 依赖 a; 假设首先构造a, spring 在一级缓存找不到 a, 则创建 a 的空 bean, 并添加到三级缓存(提前暴露), 然后尝试创建 b, 到一级缓存找不到, 则创还能 b 空 bean, 同样存入三级缓存(提前暴露), 这是 spring发现 b 竟然依赖 a, 于是在三级缓存获取到 a 的工厂对象, 进而得到a 的实例, 同时将 a 添加到二级缓存, 此时 b 构造完成, 被添加到一级缓存, 接着 a 也构造完成, 存入一级缓存.
看下来, 二级缓存貌似没什么作用, 可以去掉吗?
不可以, 因为如果抽掉二级缓存后, 每次从三级缓存拿到工厂对象, 进而生成得到空 bean, 如果两个 bean 同时依赖第三个 bean, 那么这个第三个 bean 被注入到两个 bean 中的对象将会是不同的. 为了解决这个问题, spring 引入了二级缓存
去掉二级缓存后考虑这种场景: a 依赖 b, c, 然后 b, c 都依赖 a
三级缓存为什么要添加objectFactory 工厂对象, 直接保存实例对象不行吗?
No, absolutely not. Let's assume thsi scenario: if you want to enhance one instance in the third-level cache, using the instace directly is not the way
对于spring默认无法解决的情况, 如何手动解决呢?
- 属性添加 @lazy
- 类上使用 @dependson
通过配置解决:
spring:
main:
allow-bean-definition-overriding: true
allow-circular-references: true